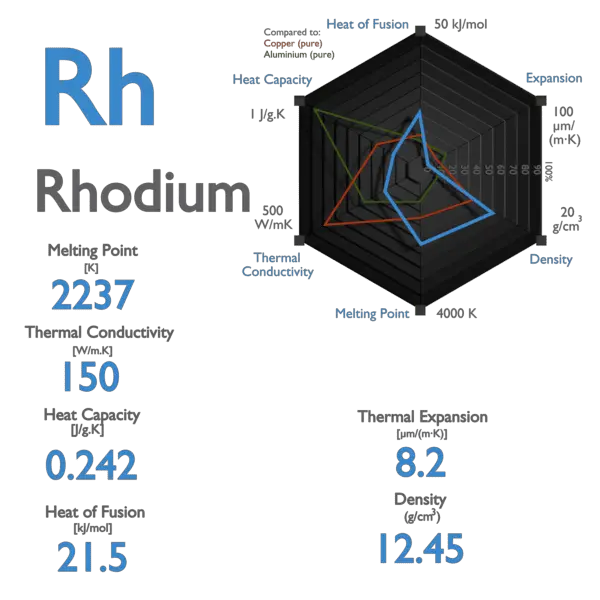
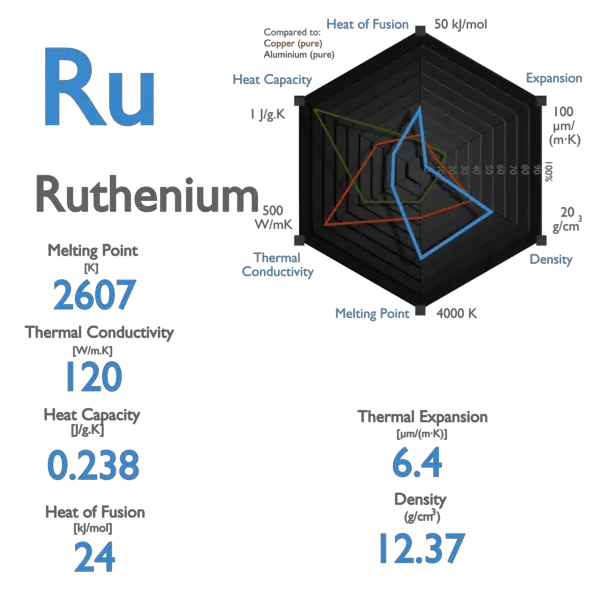
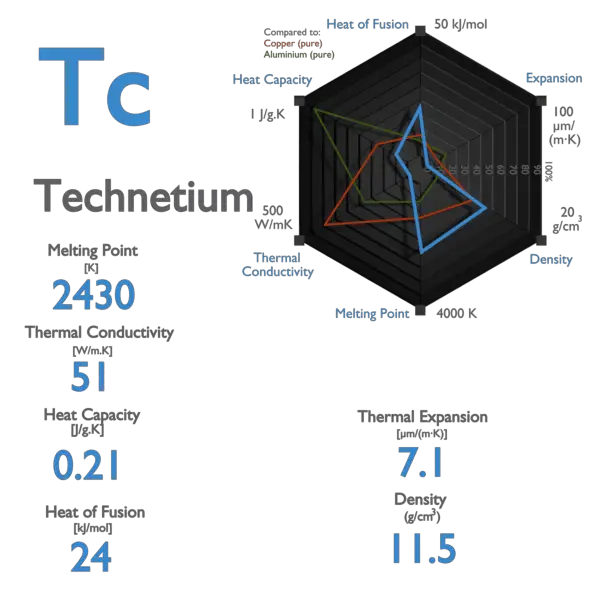
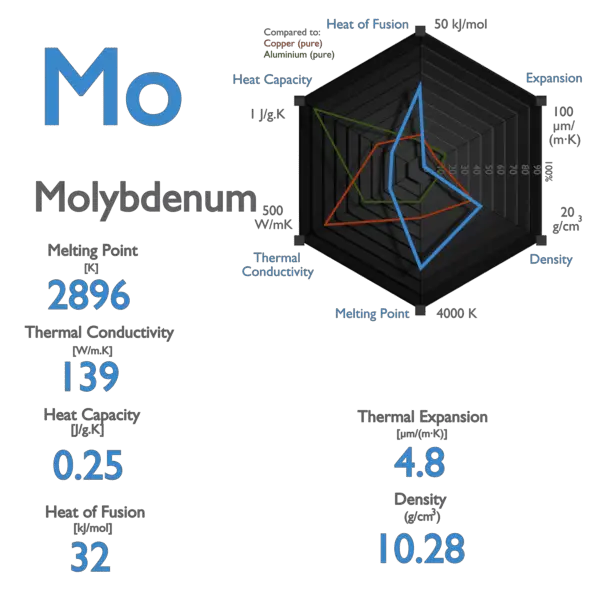
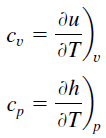Palladium – Specific Heat, Latent Heat of Fusion, Latent Heat of Vaporization
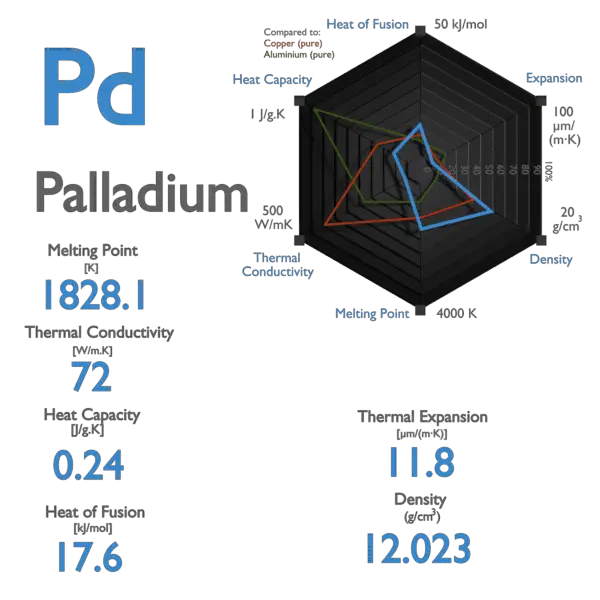
Specific heat of Palladium is 0.24 J/g K.
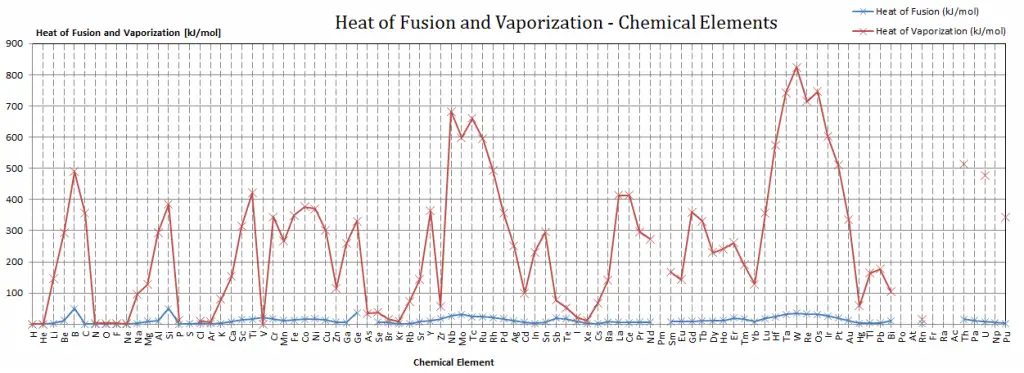
Latent Heat of Fusion of Palladium is 17.6 kJ/mol.
Latent Heat of Vaporization of Palladium is 357 kJ/mol.
Specific Heat
Specific heat, or specific heat capacity, is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics. The intensive properties cv and cp are defined for pure, simple compressible substances as partial derivatives of the internal energy u(T, v) and enthalpy h(T, p), respectively:
where the subscripts v and p denote the variables held fixed during differentiation. The properties cv and cp are referred to as specific heats(or heat capacities) because under certain special conditions, they relate the temperature change of a system to the amount of energy added by heat transfer. Their SI units are J/kg.K or J/mol K.
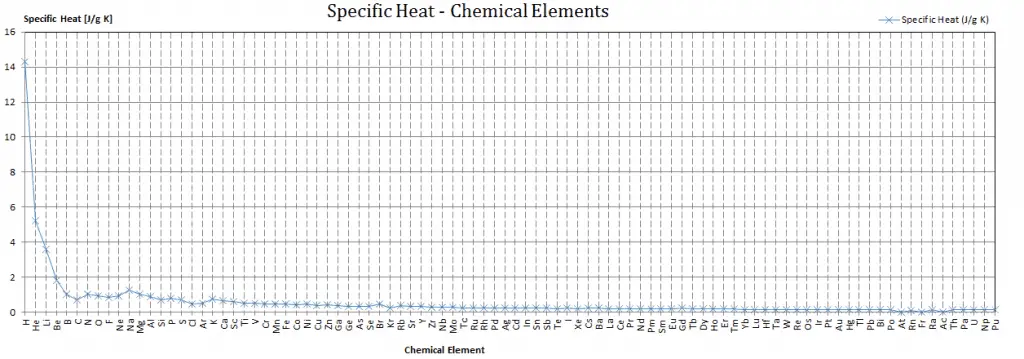
Different substances are affected to different magnitudes by the addition of heat. When a given amount of heat is added to different substances, their temperatures increase by different amounts.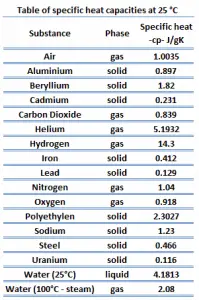
Heat capacity is an extensive property of matter, meaning it is proportional to the size of the system. Heat capacity C has the unit of energy per degree or energy per kelvin. When expressing the same phenomenon as an intensive property, the heat capacity is divided by the amount of substance, mass, or volume. Thus the quantity is independent of the size or extent of the sample.
Latent Heat of Vaporization
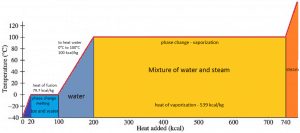
In general, when a material changes phase from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas, a certain amount of energy is involved in this change of phase. In the case of liquid to gas phase change, this amount of energy is known as the enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ∆Hvap; unit: J), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation. As an example, see the figure, which describes the phase transitions of water.
Latent heat is the amount of heat added to or removed from a substance to produce a phase change. This energy breaks down the attractive intermolecular forces and must provide the energy necessary to expand the gas (the pΔV work). When latent heat is added, no temperature change occurs. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place.
Latent Heat of Fusion
In the case of solid to liquid phase change, the change in enthalpy required to change its state is known as the enthalpy of fusion (symbol ∆Hfus; unit: J), also known as the (latent) heat of fusion. Latent heat is the amount of heat added to or removed from a substance to produce a phase change. This energy breaks down the attractive intermolecular forces and must provide the energy necessary to expand the system (the pΔV work).
The liquid phase has higher internal energy than the solid phase. This means energy must be supplied to a solid to melt it. Energy is released from a liquid when it freezes because the molecules in the liquid experience weaker intermolecular forces and have higher potential energy (a kind of bond-dissociation energy for intermolecular forces).
The temperature at which the phase transition occurs is the melting point.
When latent heat is added, no temperature change occurs. The enthalpy of fusion is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place. By convention, the pressure is assumed to be 1 atm (101.325 kPa) unless otherwise specified.
Palladium – Properties
| Element | Palladium |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 46 |
| Symbol | Pd |
| Element Category | Transition Metal |
| Phase at STP | Solid |
| Atomic Mass [amu] | 106.42 |
| Density at STP [g/cm3] | 12.023 |
| Electron Configuration | [Kr] 4d10 |
| Possible Oxidation States | +2,4 |
| Electron Affinity [kJ/mol] | 53.7 |
| Electronegativity [Pauling scale] | 2.2 |
| 1st Ionization Energy [eV] | 8.3369 |
| Year of Discovery | 1803 |
| Discoverer | Wollaston, William Hyde |
| Thermal properties | |
| Melting Point [Celsius scale] | 1554.9 |
| Boiling Point [Celsius scale] | 2963 |
| Thermal Conductivity [W/m K] | 72 |
| Specific Heat [J/g K] | 0.24 |
| Heat of Fusion [kJ/mol] | 17.6 |
| Heat of Vaporization [kJ/mol] | 357 |
Palladium in Periodic Table
–
–
–