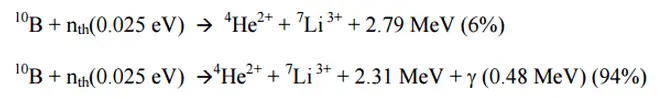Isotope 10B has many applications. Its (n,alpha) reaction cross-section for thermal neutrons is about 3840 barns (for 0.025 eV neutron) and therefore it is very good neutron absorber. In nuclear power mostly natural boron is used, but it is not an exception the use of enriched boron (by the isotope 10B). Boron as the neutron absorber has following applications:
- Chemical shim. By chemical shim, we mean that boric acid is dissolved in the coolant/moderator. Chemical shim is used for long-term reactivity control.
- Control rods. Many control rods use isotope 10B as a neutron-absorbing material.
- Safety systems. One of three primary objectives of nuclear reactor safety systems is to shut down the reactor and maintain it shutdown. Therefore all safety systems (which must ensure subcritical of the reactor after the transient) use high concentrations of boric acid.
- Burnable absorbers. Isotope 10B is widely used as the integral burnable absorber. When compared to gadolinium absorber (another commonly used burnable material), 10B has an order of magnitude smaller cross-sections. Therefore 10B compensate for reactivity longer, but not so heavily.
- A converter in neutron detectors. Neutrons are not directly ionizing, and they usually have to be converted into charged particles before they can be detected. The most common isotope for the neutron converter material is 10B.
Most of (n,alpha) reactions of thermal neutrons are 10B(n,alpha)7Li reactions accompanied by 0.48 MeV gamma emission.
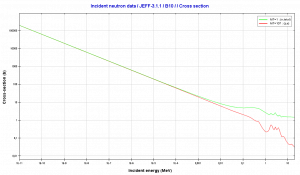
Source: JANIS (Java-based Nuclear Data Information Software); The JEFF-3.1.1 Nuclear Data Library