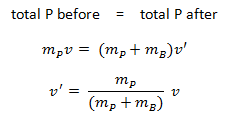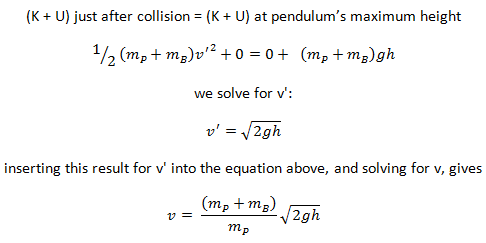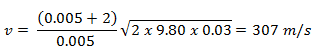Ballistic Pendulum
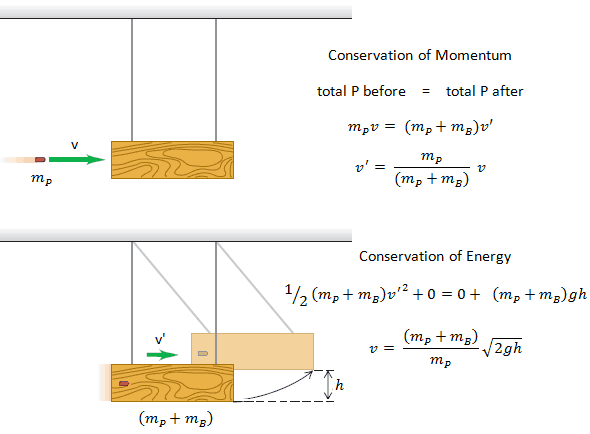
A ballistic pendulum is a device for measuring the velocity of a projectile, such as a bullet. The ballistic pendulum is a kind of “transformer,” exchanging the high speed of a light object (the bullet) for the low speed of a massive object (the block). When a bullet is fired into the block, its momentum is transferred to the block. The bullet’s momentum can be determined from the amplitude of the pendulum swing.
When the bullet is embedding itself in the block, it occurs so quickly that the block does not move appreciably. The supporting strings remain nearly vertical, so negligible external horizontal force acts on the bullet–block system, and the horizontal component of momentum is conserved. However, mechanical energy is not conserved during this stage because a nonconservative force does work (the force of friction between bullet and block).
In the second stage, the bullet and block move together. The only forces acting on this system are gravity (a conservative force) and string tensions (which do not work). Thus, as the block swings, mechanical energy is conserved. Momentum is not conserved during this stage because there is a net external force (the forces of gravity and string tension don’t cancel when the strings are inclined).
Equations governing the ballistic pendulum
In the first stage, momentum is conserved, and therefore:
where v is the initial velocity of the projectile of mass mP. v’ is the velocity of the block and embedded projectile (both of mass mP + mB) just after the collision, before they have moved significantly.
In the second stage, mechanical energy is conserved. We choose y = 0 when the pendulum hangs vertically and then y = h when the block and embedded projectile system reach maximum height. The system swings up and comes to rest for an instant at a height y, where its kinetic energy is zero, and the potential energy is (mP + mB)gh. Thus we write the law of conservation of energy:
which is the initial velocity of the projectile and our final result.
When we use some realistic numbers:
- mP = 5 g
- mB = 2 kg
- h = 3 cm
- v = ?
then we have: