The capacity factor is defined as the ratio of actual energy produced over a period and the maximum energy that could be produced over that period. The capacity factor describes the basic performance characteristics of a given energy source.
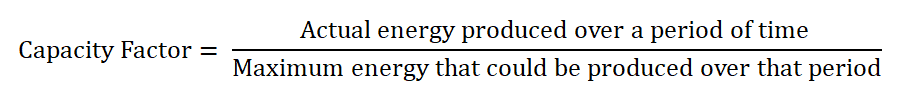
So if a plant was operated for 200 days at full power days in the period of 1 year, then the CF = 200 / 365 = 0.55, or 55%. If the plant was available for 365 days but only at 55% of rated power, the capacity factor would be again 55%.
Nuclear power plants have the highest capacity factor of any other energy source — more than 92% of the time. In general, nuclear power plants (NPPs) have been considered baseload sources of electricity as they rely on technology with low variable costs and high fixed costs.
For fossil sources, the capacity factor is affected by the way the plant is operated. Some sources are operated intentionally as peak sources (with lower CP) and some as baseload sources (with higher CP).
The capacity factor of a wind turbine is its average power output divided by its maximum power capability. On land, capacity factors range from 0.26 to 0.52. The average 2019 capacity factor for projects built between 2014 and 2018 was 41%. In the U.S., the fleetwide average capacity factor was 35%.
The factor is the photovoltaic power station, which supplies power to the electricity grid from a large-scale photovoltaic system (PV system) At a low capacity range. An inherent limit to its capacity factor comes from its requirement of daylight, preferably with a sun unobstructed by clouds, smoke, or smog, and shade from trees and building structures. Since the amount of sunlight varies with the time of the day and the seasons of the year, the capacity factor is typically computed annually.
For our calculations, we used capacity factors (an actual electrical energy output over a given period to the maximum possible electrical energy output over that period) for energy sources:
-
- Nuclear power – 85%
- Geothermal power – 70%
- Biomass power plant- 50%
- Gas – combined cycle – 50%
- Coal power plant – 40%
- Hydropower – 40%
- Wind power – 35%
- Solar power – 20%