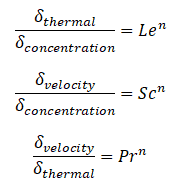Velocity Boundary Layer
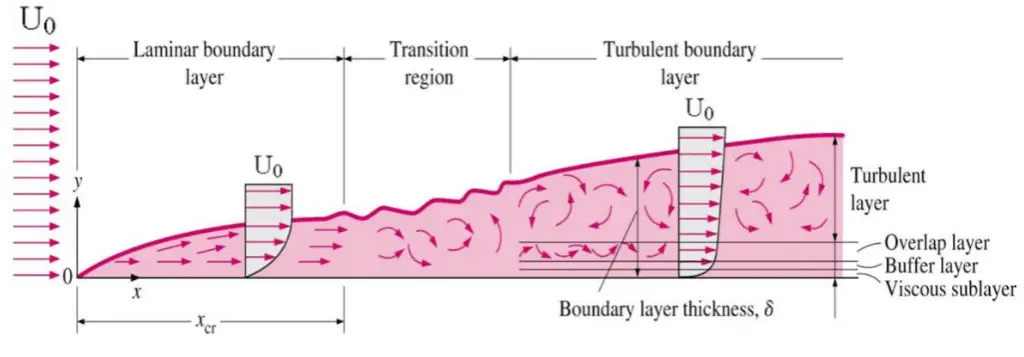
In general, when a fluid flows over a stationary surface, e.g., the flat plate, the bed of a river, or the pipe wall, the fluid touching the surface is brought to rest by the shear stress at the wall. The boundary layer is the region in which flow adjusts from zero velocity at the wall to a maximum in the mainstream of the flow. The concept of boundary layers is important in all viscous fluid dynamics and the theory of heat transfer.
Basic characteristics of all laminar and turbulent boundary layers are shown in the developing flow over a flat plate. The stages of the formation of the boundary layer are shown in the figure below:
Boundary layers may be either laminar or turbulent, depending on the value of the Reynolds number.
See also: Boundary Layer
Thermal Boundary Layer
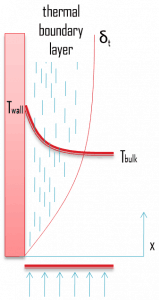 Similarly, as a velocity boundary layer develops when fluid flows over a surface, a thermal boundary layer must develop if the bulk temperature and surface temperature differ. Consider flow over an isothermal flat plate at a constant temperature of Twall. At the leading edge, the temperature profile is uniform with Tbulk. Fluid particles that come into contact with the plate achieve thermal equilibrium at the plate’s surface temperature. At this point, energy flow occurs at the surface purely by conduction. These particles exchange energy with those in the adjoining fluid layer (by conduction and diffusion), and temperature gradients develop in the fluid. The fluid region in which these temperature gradients exist is the thermal boundary layer. Its thickness, δt, is typically defined as the distance from the body at which the temperature is 99% of the temperature found from an inviscid solution. With increasing distance from the leading edge, the effects of heat transfer penetrate farther into the stream, and the thermal boundary layer grows.
Similarly, as a velocity boundary layer develops when fluid flows over a surface, a thermal boundary layer must develop if the bulk temperature and surface temperature differ. Consider flow over an isothermal flat plate at a constant temperature of Twall. At the leading edge, the temperature profile is uniform with Tbulk. Fluid particles that come into contact with the plate achieve thermal equilibrium at the plate’s surface temperature. At this point, energy flow occurs at the surface purely by conduction. These particles exchange energy with those in the adjoining fluid layer (by conduction and diffusion), and temperature gradients develop in the fluid. The fluid region in which these temperature gradients exist is the thermal boundary layer. Its thickness, δt, is typically defined as the distance from the body at which the temperature is 99% of the temperature found from an inviscid solution. With increasing distance from the leading edge, the effects of heat transfer penetrate farther into the stream, and the thermal boundary layer grows.
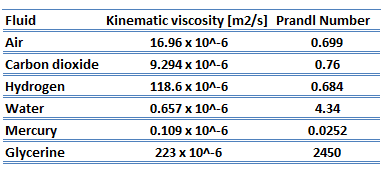 The ratio of these two thicknesses (velocity and thermal boundary layers) is governed by the Prandtl number, defined as the ratio of momentum diffusivity to thermal diffusivity. A Prandtl number of unity indicates that momentum and thermal diffusivity are comparable, and velocity and thermal boundary layers almost coincide with each other. If the Prandtl number is less than 1, which is the case for air at standard conditions, the thermal boundary layer is thicker than the velocity boundary layer. If the Prandtl number is greater than 1, the thermal boundary layer is thinner than the velocity boundary layer. Air at room temperature has a Prandtl number of 0.71, and for water, at 18°C, it is around 7.56, which means that the thermal diffusivity is more dominant for air than for water.
The ratio of these two thicknesses (velocity and thermal boundary layers) is governed by the Prandtl number, defined as the ratio of momentum diffusivity to thermal diffusivity. A Prandtl number of unity indicates that momentum and thermal diffusivity are comparable, and velocity and thermal boundary layers almost coincide with each other. If the Prandtl number is less than 1, which is the case for air at standard conditions, the thermal boundary layer is thicker than the velocity boundary layer. If the Prandtl number is greater than 1, the thermal boundary layer is thinner than the velocity boundary layer. Air at room temperature has a Prandtl number of 0.71, and for water, at 18°C, it is around 7.56, which means that the thermal diffusivity is more dominant for air than for water.
Similarly, as for Prandtl Number, the Lewis number physically relates the relative thickness of the thermal layer and mass-transfer (concentration) boundary layer. The Schmidt number physically relates the relative thickness of the velocity boundary layer and mass-transfer (concentration) boundary layer.
where n = 1/3 for most applications in all three relations. These relations, in general, are applicable only for laminar flow and are not applicable to turbulent boundary layers since turbulent mixing in this case may dominate the diffusion processes.