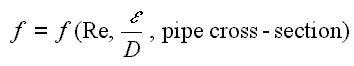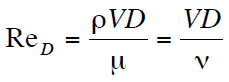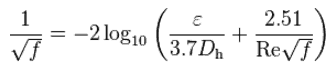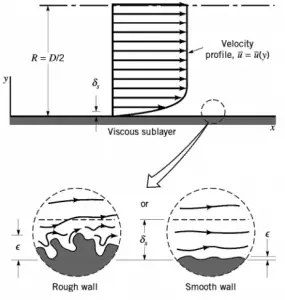
https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=4681366
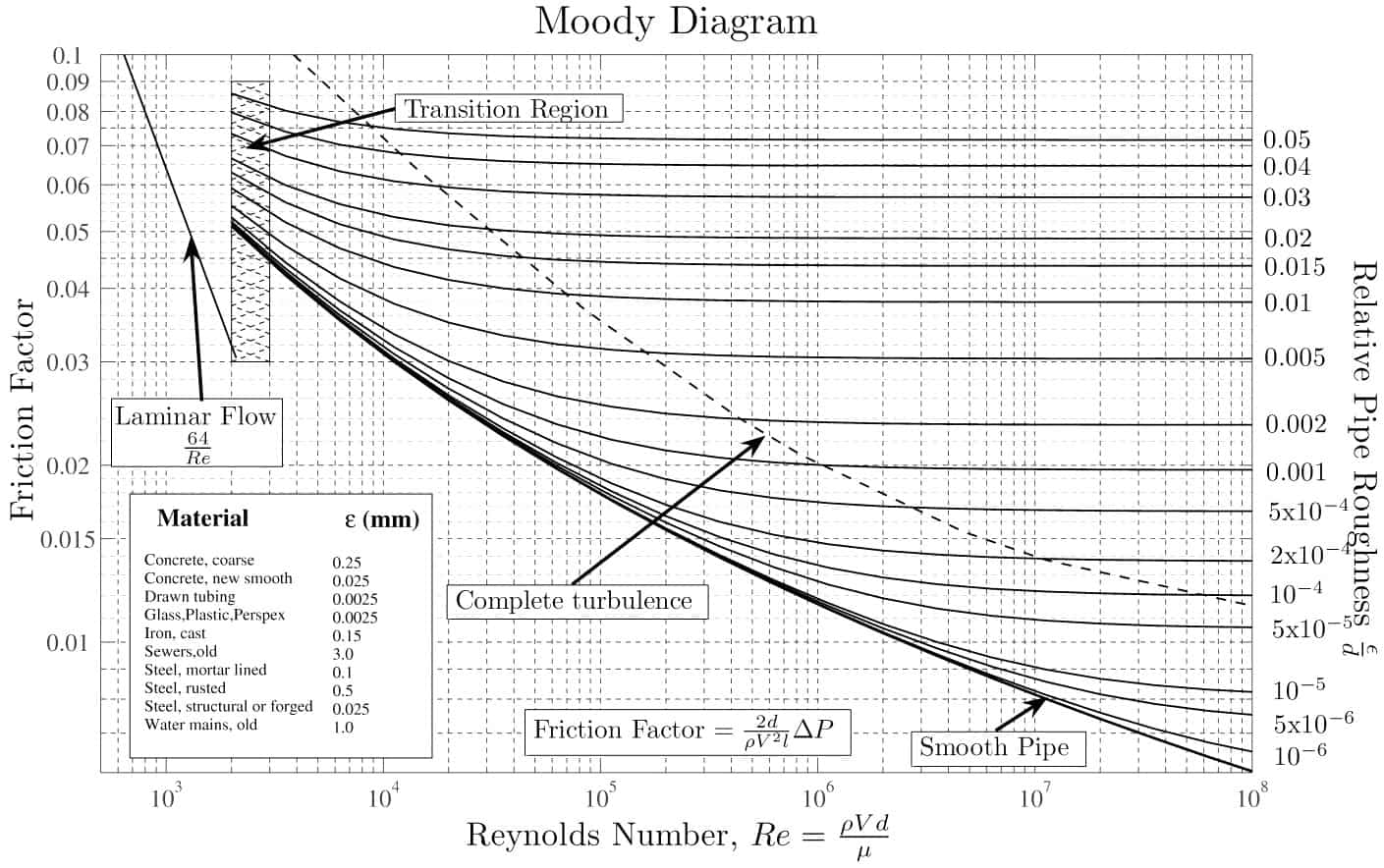
Example: Moody Diagram
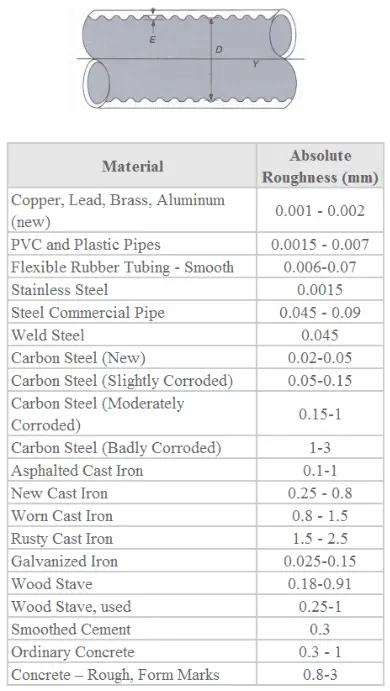
Using the Moody diagram, determine the friction factor (fD) for fluid flow in a pipe of 700mm in diameter with a Reynolds number of 50 000 000 and an absolute roughness of 0.035 mm.
Solution:
The relative roughness is equal to ε = 0.035 / 700 = 5 x 10-5. Using the Moody Chart, a Reynolds number of 50 000 000 intersects the curve corresponding to a relative roughness of 5 x 10-5 at a friction factor of 0.011.
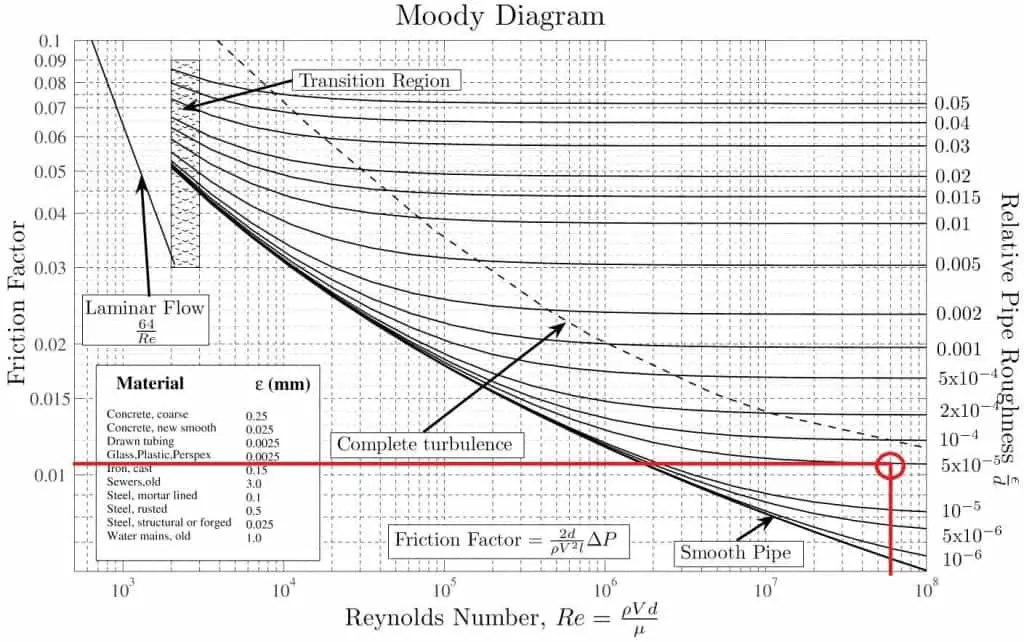
Source: Donebythesecondlaw at the English language Wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=4681366
Darcy Friction Factor for various flow regime
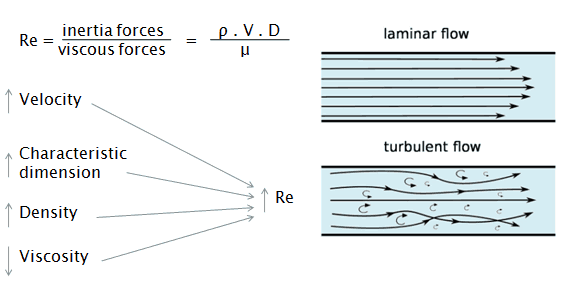
The most common classification of flow regimes is according to the Reynolds number. The Reynolds number is a dimensionless number comprised of the physical characteristics of the flow, and it determines whether the flow is laminar or turbulent. An increasing Reynolds number indicates increasing turbulence of flow. As can be seen from the Moody chart, the Darcy friction factor also depends on the flow regime (i.e., on the Reynolds number).