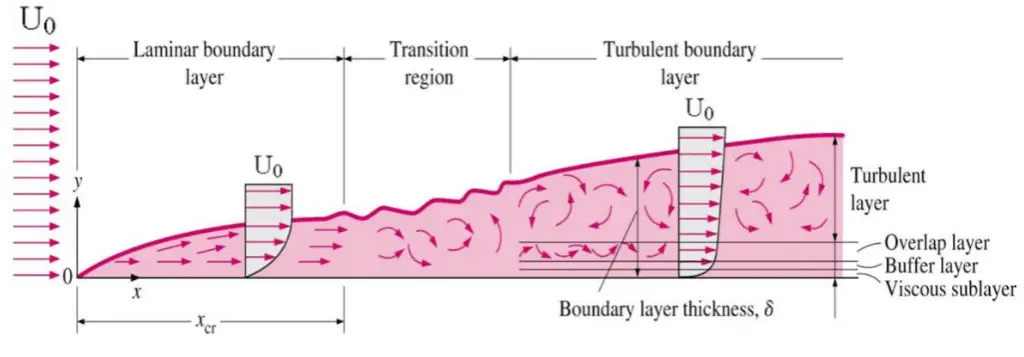
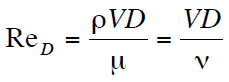The concept of boundary layers is important in all viscous fluid dynamics, aerodynamics, and heat transfer theory. Basic characteristics of all laminar and turbulent boundary layers are shown in the developing flow over a flat plate. The stages of the formation of the boundary layer are shown in the figure below:
Boundary layers may be either laminar or turbulent, depending on the value of the Reynolds number. Also, here the Reynolds number represents the ratio of inertia forces to viscous forces and is a convenient parameter for predicting if a flow condition will be laminar or turbulent. It is defined as:
in which V is the mean flow velocity, D is a characteristic linear dimension, ρ fluid density, μ dynamic viscosity, and ν kinematic viscosity.
The boundary layer is laminar for lower Reynolds numbers, and the streamwise velocity uniformly changes as one moves away from the wall, as shown on the left side of the figure. As the Reynolds number increases (with x), the flow becomes unstable. Finally, the boundary layer is turbulent for higher Reynolds numbers, and the streamwise velocity is characterized by unsteady (changing with time) swirling flows inside the boundary layer.
The transition from laminar to turbulent boundary layer occurs when Reynolds number at x exceeds Rex ~ 500,000. The transition may occur earlier, but it is dependent especially on the surface roughness. The turbulent boundary layer thickens more rapidly than the laminar boundary layer due to increased shear stress at the body surface.
See also: Boundary layer thickness.
See also: Tube in crossflow – external flow.
Special reference: Schlichting Herrmann, Gersten Klaus. Boundary-Layer Theory, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2000, ISBN: 978-3-540-66270-9