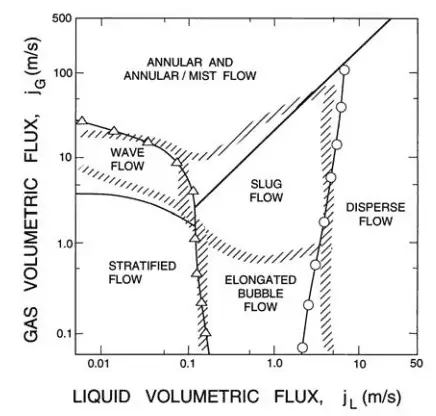
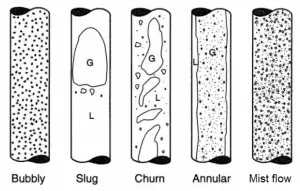
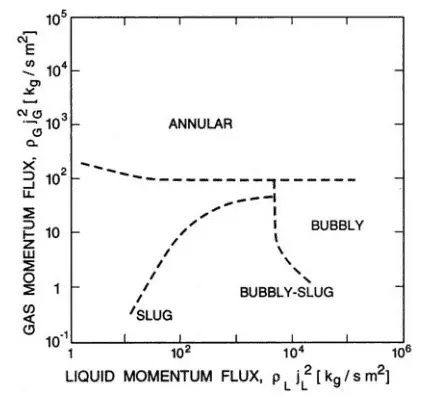
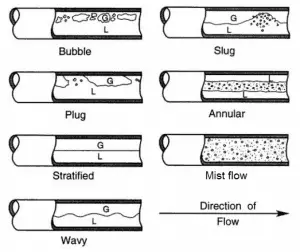
Mist Flow – Vertical Tubes
Mist flow is a flow regime of two-phase gas-liquid flow. It occurs at very high flow rates and very high flow quality. This condition causes the liquid film flowing on the channel wall to be thinned by the shear of the gas core on the interface until it becomes unstable and is destroyed. The flow core in the mist flow entrains all the liquid as droplets in the gas phase. Droplets may wet the tube wall, but this occurs intermittently and only locally. In the heated channel, the presence of a mist flow regime is accompanied by significantly higher wall temperatures and high fluctuation of wall temperatures.
Mist Flow – Horizontal Tubes
Mist flow is a flow regime of two-phase gas-liquid flow. It occurs at very high flow rates and very high flow quality. This condition causes the liquid film flowing on the channel wall to be thinned by the shear of the gas core on the interface until it becomes unstable and is destroyed. The flow core in the mist flow entrains all the liquid as droplets in the gas phase. Droplets may wet the tube wall, but this occurs intermittently and only locally. In the heated channel, the presence of a mist flow regime is accompanied by significantly higher wall temperatures and high fluctuation of wall temperatures.