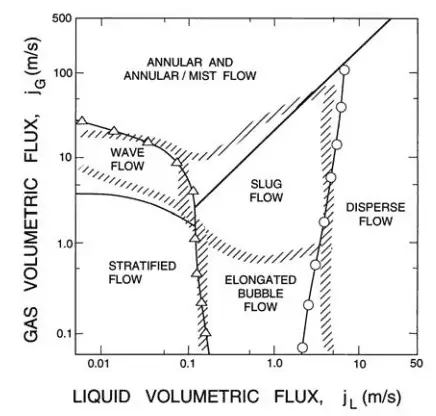
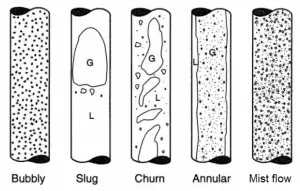
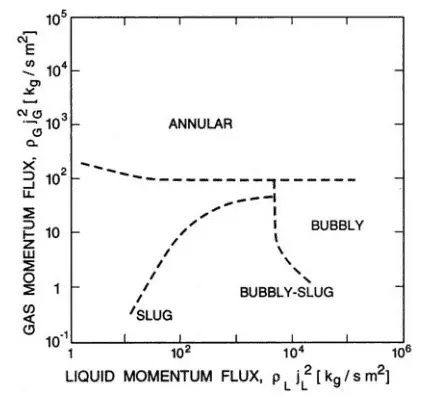
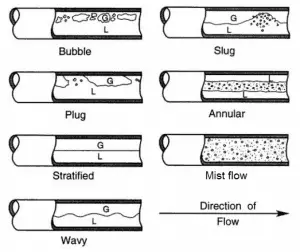
Slug Flow – Vertical Tubes
Increasing void fraction in bubbly flow causes agglomeration of bubbles into larger plugs and slugs. These slugs are similar in dimension to the tube diameter. These slugs travel at a speed that is a substantial fraction of the gas velocity and occur intermittently. Since these large gas slugs are separated from one another by slugs of liquid, they cause large pressure and liquid flow rate fluctuations. In some cases, a downward flow can be observed near the tube wall, even though the net flow of fluid is upward. This is caused by the gravitational force.
Plug Flow and Slug Flow – Horizontal Tubes
Further increase in the gas velocity causes that waves reach the top of the tube. Whether the flow will be plug or slug flow depends especially on the void fraction that causes agglomeration of bubbles into larger plugs and slugs. In the plug flow, the diameters of the bubbles are smaller than the tube. Slugs are similar in dimension to the tube diameter. The slugs travel at a speed that is a substantial fraction of the gas velocity and occur intermittently. Since these large gas slugs are separated from one another by slugs of liquid, they cause large pressure and liquid flow rate fluctuations.