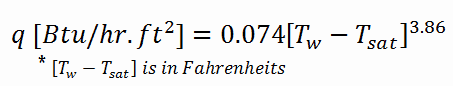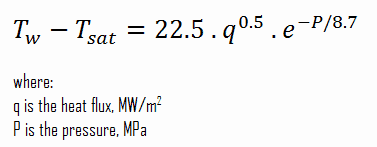Bulk boiling may occur when system temperature increases or pressure drops to the boiling point. At this point, the bubbles entering the coolant channel will not collapse.
The bubbles will tend to join together and form bigger steam bubbles. Steam bubbles are then propelled through the liquid by buoyancy forces, eventually escaping from a free surface.
Bulk Boiling in BWRs
 In BWRs, coolant boiling occurs at normal operation and is a very desired phenomenon. Typical flow qualities in BWR cores are on the order of 10 to 20 %. A boiling water reactor is cooled and moderated by water like a PWR, but at a lower pressure (7MPa), which allows the water to boil inside the pressure vessel producing the steam that runs the turbines. Evaporation, therefore, occurs directly in fuel channels. Therefore BWRs are the best example for this area because coolant evaporation occurs at normal operation, and it is a very desired phenomenon.
In BWRs, coolant boiling occurs at normal operation and is a very desired phenomenon. Typical flow qualities in BWR cores are on the order of 10 to 20 %. A boiling water reactor is cooled and moderated by water like a PWR, but at a lower pressure (7MPa), which allows the water to boil inside the pressure vessel producing the steam that runs the turbines. Evaporation, therefore, occurs directly in fuel channels. Therefore BWRs are the best example for this area because coolant evaporation occurs at normal operation, and it is a very desired phenomenon.
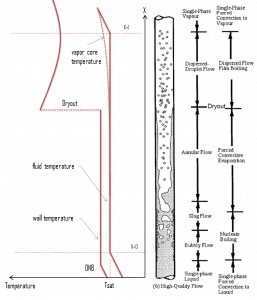
In BWRs, there is a phenomenon of the highest importance in reactor safety. This phenomenon is known as the “dry-out” and is directly associated with changes in flow pattern during evaporation in the high-quality region. At normal, the fuel surface is effectively cooled by boiling coolant. However, when the heat flux exceeds a critical value (CHF – critical heat flux), the flow pattern may reach the dry-out conditions (the thin film of liquid disappears). The heat transfer from the fuel surface into the coolant is deteriorated due to a drastically increased fuel surface temperature.
Bulk Boiling in PWRs
For PWRs at normal operation, there is compressed liquid water inside the reactor core, loops, and steam generators. The pressure is maintained at approximately 16MPa. At this pressure, water boils at approximately 350°C(662°F), which gives a subcooling margin (the difference between the pressurizer temperature and the coolant outlet temperature in the reactor core) of 30 °C. Noteworthy, this subcooling margin concerns the bulk temperature since bulk boiling is in any case prohibited.
Subcooling margin is an important safety parameter of PWRs since the bulk boiling in the reactor core must be excluded. The basic design of the pressurized water reactor includes such a requirement that the coolant (water) in the reactor coolant system must not boil. To achieve this, the coolant in the reactor coolant system is maintained at a pressure sufficiently high that boiling does not occur at the coolant temperatures experienced while the plant is operating or in an analyzed transient.
As was calculated in the example, the surface temperature TZr,1 = 325°C ensures that even subcooled boiling does not occur. Note that subcooled boiling requires TZr,1 = Tsat. Since the inlet temperatures of the water are usually about 290°C (554°F), it is obvious this example corresponds to the lower part of the core. At higher core elevations, the bulk temperature may reach up to 330°C. The temperature difference of 29°C causes the subcooled surface boiling may occur (330°C + 29°C > 350°C). On the other hand, nucleate boiling at the surface effectively disrupts the stagnant layer. Therefore, nucleate boiling significantly increases the ability of a surface to transfer thermal energy to the bulk fluid. As a result, the convective heat transfer coefficient significantly increases, and therefore at higher elevations, the temperature difference (TZr,1 – Tbulk) significantly decreases.
Nucleate Boiling – Flow Boiling
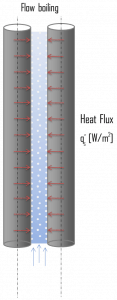 In flow boiling (or forced convection boiling), fluid flow is forced over a surface by external means such as a pump, as well as by buoyancy effects. Therefore, flow boiling is always accompanied by other convection effects. Conditions depend strongly on geometry, involving external flow over heated plates and cylinders or internal (duct) flow. In nuclear reactors, most boiling regimes are just forced convection boiling. The flow boiling is also classified as either external and internal flow boiling, depending on whether the fluid is forced to flow over a heated surface or inside a heated channel.
In flow boiling (or forced convection boiling), fluid flow is forced over a surface by external means such as a pump, as well as by buoyancy effects. Therefore, flow boiling is always accompanied by other convection effects. Conditions depend strongly on geometry, involving external flow over heated plates and cylinders or internal (duct) flow. In nuclear reactors, most boiling regimes are just forced convection boiling. The flow boiling is also classified as either external and internal flow boiling, depending on whether the fluid is forced to flow over a heated surface or inside a heated channel.
Internal flow boiling is much more complicated in nature than external flow boiling because there is no free surface for the vapor to escape, and thus both the liquid and the vapor are forced to flow together. The two-phase flow in a tube exhibits different flow boiling regimes, depending on the relative amounts of the liquid and the vapor phases. Therefore internal forced convection boiling is commonly referred to as two-phase flow.
Nucleate Boiling Correlations – Flow Boiling
McAdams Correlation
In fully developed nucleate boiling with saturated coolant, the wall temperature is determined by local heat flux and pressure and is only slightly dependent on the Reynolds number. For subcooled water at absolute pressures between 0.1 – 0.6 MPa, McAdams correlation gives:
Thom Correlation
The Thom correlation is for the flow boiling (subcooled or saturated at pressures up to about 20 MPa) under conditions where the nucleate boiling contribution predominates over forced convection. This correlation is useful for a rough estimation of expected temperature difference given the heat flux:
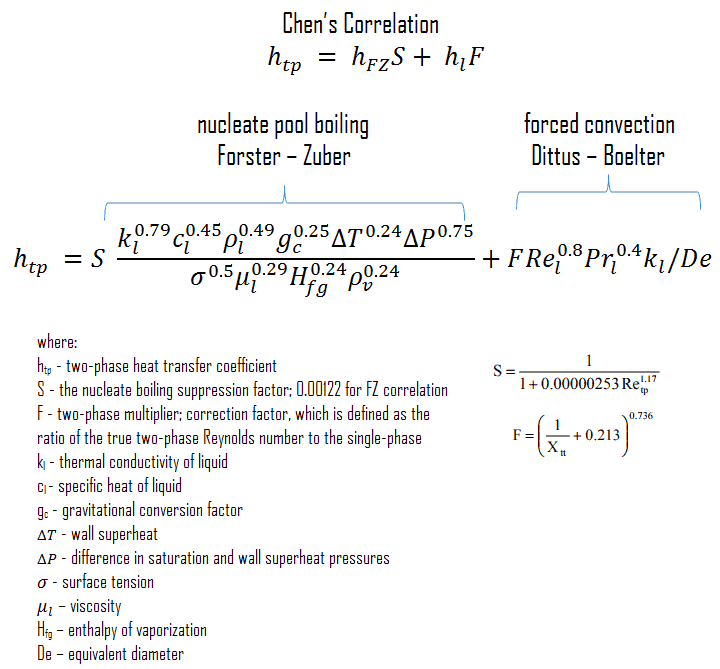
Chen’s Correlation
In 1963, Chen proposed the first flow boiling correlation for evaporation in vertical tubes to attain widespread use. Chen’s correlation includes both the heat transfer coefficients due to nucleate boiling as well as forced convective mechanisms. It must be noted at higher vapor fractions. The heat transfer coefficient varies strongly with the flow rate, and the flow velocity in a core can be very high, causing very high turbulences. This heat transfer mechanism has been referred to as “forced convection evaporation”. No adequate criteria have been established to determine the transition from nucleate boiling to forced convection vaporization. However, a single correlation that is valid for both nucleate boiling and forced convection vaporization has been developed by Chen for saturated boiling conditions and extended to include subcooled boiling by others. Chen proposed a correlation where the heat transfer coefficient is the sum of a forced convection component and a nucleate boiling component. It must be noted the nucleate pool boiling correlation of Forster and Zuber (1955) is used to calculate the nucleate boiling heat transfer coefficient, hFZ, and the turbulent flow correlation of Dittus-Boelter (1930) is used to calculate the liquid-phase convective heat transfer coefficient, hl.
The nucleate boiling suppression factor, S, is the ratio of the effective superheats to wall superheat. It accounts for decreased boiling heat transfer because the effective superheat across the boundary layer is less than the superheat based on wall temperature. The two-phase multiplier, F, is a function of the Martinelli parameter χtt.
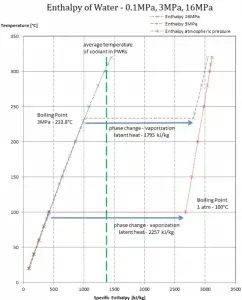
 The change from the liquid to the vapor state due to boiling is sustained by heat transfer from the solid surface; conversely, condensation of a vapor to the liquid state results in heat transfer to the solid surface. Boiling and condensation differ from other forms of convection in that they depend on the latent heat of vaporization, which is very high for common
The change from the liquid to the vapor state due to boiling is sustained by heat transfer from the solid surface; conversely, condensation of a vapor to the liquid state results in heat transfer to the solid surface. Boiling and condensation differ from other forms of convection in that they depend on the latent heat of vaporization, which is very high for common