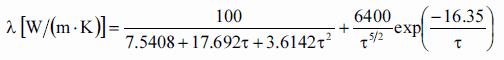 Most PWRs use uranium fuel, which is in the form of uranium dioxide. Uranium dioxide is a black semiconducting solid with very low thermal conductivity. On the other hand, uranium dioxide has a very high melting point and has well-known behavior. The UO2 is pressed into pellets, and these pellets are then sintered into the solid.
Most PWRs use uranium fuel, which is in the form of uranium dioxide. Uranium dioxide is a black semiconducting solid with very low thermal conductivity. On the other hand, uranium dioxide has a very high melting point and has well-known behavior. The UO2 is pressed into pellets, and these pellets are then sintered into the solid.
These pellets are then loaded and encapsulated within a fuel rod (or fuel pin) made of zirconium alloys due to their very low absorption cross-section (unlike stainless steel). The surface of the tube, which covers the pellets, is called fuel cladding, and fuel rods are the base element of a fuel assembly.
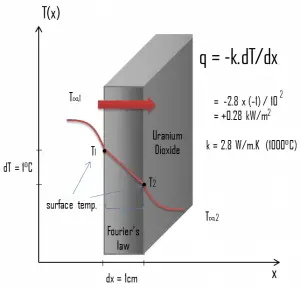
The thermal conductivity of uranium dioxide is very low compared with metal uranium, uranium nitride, uranium carbide, and zirconium cladding material. Thermal conductivity is one of the parameters which determine the fuel centerline temperature. This low thermal conductivity can result in localized overheating in the fuel centerline, and therefore this overheating must be avoided. Overheating of the fuel is prevented by maintaining the steady-state peak linear heat rate (LHR) or the Heat Flux Hot Channel Factor – FQ(z) below the level at which fuel centerline melting occurs. Expansion of the fuel pellet upon centerline melting may cause the pellet to stress the cladding to the point of failure.
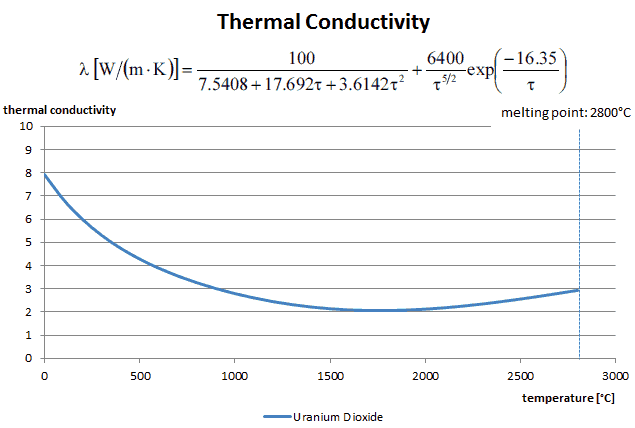
Thermal conductivity of solid UO2 with a density of 95% is estimated by the following correlation [Klimenko; Zorin]:
where τ = T/1000. The uncertainty of this correlation is +10% in the range from 298.15 to 2000 K and +20% in the range from 2000 to 3120 K.
Special reference: Thermal and Nuclear Power Plants/Handbook ed. by A.V. Klimenko and V.M. Zorin. MEI Press, 2003.
Special reference: Thermophysical Properties of Materials For Nuclear Engineering: A Tutorial and Collection of Data. IAEA-THPH, IAEA, Vienna, 2008. ISBN 978–92–0–106508–7.
Thermal Conductivity of Nonmetals
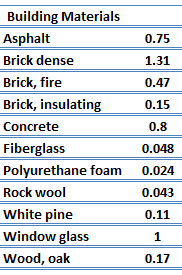 For nonmetallic solids, k is determined primarily by kph, which increases as the frequency of interactions between the atoms and the lattice decreases. Lattice thermal conduction is the dominant thermal conduction mechanism in nonmetals, if not the only one. In solids, atoms vibrate about their equilibrium positions (crystal lattice). The vibrations of atoms are not independent of each other but are rather strongly coupled with neighboring atoms. The regularity of the lattice arrangement has an important effect on kph, with crystalline (well-ordered) materials like quartz having a higher thermal conductivity than amorphous materials like glass. At sufficiently high temperatures kph ∝ 1/T.
For nonmetallic solids, k is determined primarily by kph, which increases as the frequency of interactions between the atoms and the lattice decreases. Lattice thermal conduction is the dominant thermal conduction mechanism in nonmetals, if not the only one. In solids, atoms vibrate about their equilibrium positions (crystal lattice). The vibrations of atoms are not independent of each other but are rather strongly coupled with neighboring atoms. The regularity of the lattice arrangement has an important effect on kph, with crystalline (well-ordered) materials like quartz having a higher thermal conductivity than amorphous materials like glass. At sufficiently high temperatures kph ∝ 1/T.
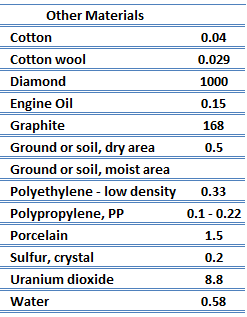 The quanta of the crystal vibrational field are referred to as ‘‘phonons.’’ A phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, like solids and some liquids. Phonons play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter, like thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. In fact, for crystalline, nonmetallic solids such as diamond, kph can be quite large, exceeding values of k associated with good conductors, such as aluminum. In particular, diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity (k = 1000 W/m.K) of any bulk material.
The quanta of the crystal vibrational field are referred to as ‘‘phonons.’’ A phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, like solids and some liquids. Phonons play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter, like thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity. In fact, for crystalline, nonmetallic solids such as diamond, kph can be quite large, exceeding values of k associated with good conductors, such as aluminum. In particular, diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity (k = 1000 W/m.K) of any bulk material.