In short, effective shielding of gamma radiation is in most cases based on use of materials with two following material properties:
- the high-density of material
- the high atomic number of material (high Z materials)
Although water is neither high density nor high Z material, it is commonly used as gamma shields. Water provides a radiation shielding of fuel assemblies in a spent fuel pool during storage or transports from and into the reactor core. Although water is a low-density material and low Z material, it is commonly used in nuclear power plants because these disadvantages can be compensated with increased thickness.
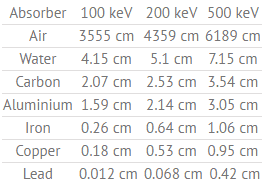
Half Value Layer of Water
The half-value layer expresses the thickness of absorbing material needed to reduce the incident radiation intensity by a factor of two.
Table of Half Value Layers (in cm) for a different materials at gamma ray energies of 100, 200 and 500 keV.