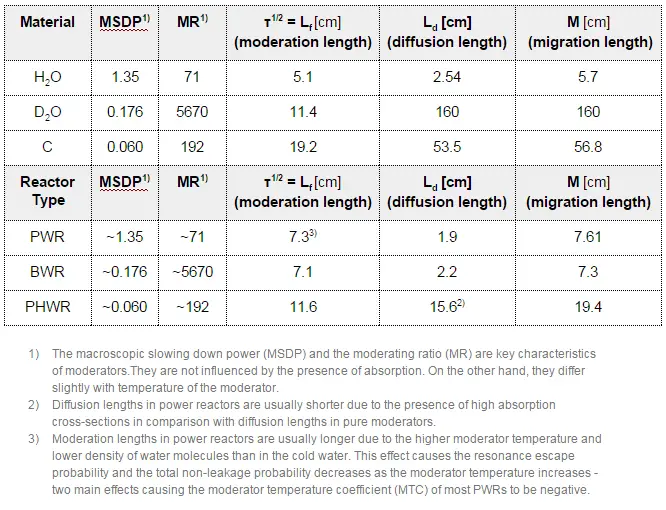
The neutron moderator, which is important in thermal reactors, is used to moderate, that is, to slow down neutrons from fission to thermal energies. Nuclei with low mass numbers are most effective for this purpose, so the moderator is always a low-mass-number material. Commonly used moderators include regular (light) water (roughly 75% of the world’s reactors), solid graphite (20% of reactors), and heavy water (5% of reactors).
In most nuclear reactors, water is both a coolant and a moderator. The moderation occurs especially on hydrogen nuclei. In the case of the hydrogen (A = 1) as the target nucleus, the incident neutron can be completely stopped – it has the highest average logarithmic energy decrement of all nuclei. On the other hand, hydrogen nuclei have a relatively higher absorption cross-section. Therefore water is not the best moderator according to the moderating ratio.