Some of the properties of crystalline solids depend on the crystal structure of the material and how atoms, ions, or molecules are spatially arranged. A crystal lattice is a repeating pattern of mathematical points that extends throughout space, and the forces of chemical bonding cause this repetition. This repeated pattern controls properties like strength, ductility, density, conductivity (property of conducting or transmitting heat, electricity, etc.), and shape. There are 14 general types of such patterns known as Bravais lattices. Three relatively simple crystal structures are found for most of the common metals.
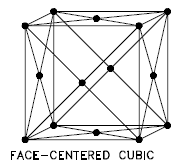
Face-centered Cubic
In a face-centered cubic (fcc) arrangement of atoms, the unit cell consists of eight atoms at the corners of a cube and one atom at the center of each of the faces of the cube. In an fcc arrangement, a unit cell contains (8 corner atoms × ⅛) + (6 face atoms × ½) = 4 atoms. This structure, along with its hexagonal relative (hcp), has the most efficient packing (74%). Metals containing FCC structures include austenite, aluminum, copper, lead, silver, gold, nickel, platinum, and thorium, and these metals possess low strength and high ductility.