Line defects are generally many atoms in length, which are called dislocations and occur in crystalline materials only. Dislocations are especially important in materials science because they help determine the mechanical strength of materials. There are two basic types of dislocations: edge dislocation and screw dislocation. Mixed dislocations, combining aspects of both types, are also common. It is important to note that dislocations cannot end inside a crystal, and they must end at a crystal edge or other dislocation or close back on themselves.
Early materials studies led to the computation of the theoretical strengths of perfect crystals. But these theoretical strengths were many times greater than those measured. During the 1930s, it was theorized that this discrepancy in mechanical strengths could be explained by a type of linear crystalline defect that has come to be known as a dislocation. The term ‘dislocation’ referring to a defect on the atomic scale was coined by G. I. Taylor in 1934.
Edge Dislocation
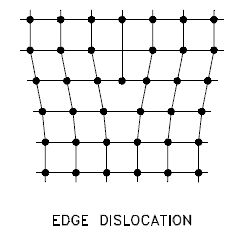
Edge dislocation centers around the edge dislocation line defined along the end of the extra half-plane of atoms. The imperfection may extend in a straight line through the crystal or follow an irregular path. It may also be short, extending only a small distance into the crystal, causing a slip of one atomic distance along the glide plane (the direction the edge imperfection is moving). Macroscopic plastic deformation simply corresponds to permanent deformation that results from the movement of dislocations or slips in response to applied shear stress. Dislocations can move if the atoms from one of the surrounding planes break their bonds and rebond with the atoms at the terminating edge. Understanding dislocation movement is key to understanding why dislocations allow deformation to occur at much lower stress than in a perfect crystal. Dislocation motion is analogous to the movement of a caterpillar. The caterpillar would have to exert a large force to move its entire body at once. Instead, it moves the rear portion of its body forward a small amount and creates a hump. The hump moves forward and eventually moves all of the body forward by a small amount. The slip occurs when the crystal is subjected to stress, and the dislocation moves through it until it reaches the edge or is arrested by another dislocation.
Screw Dislocation
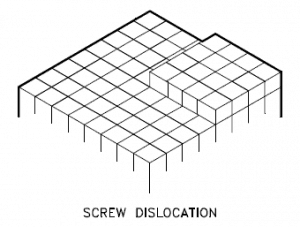
Screw dislocations can be produced by tearing the crystal parallel to the slip direction. If a screw dislocation is followed around a complete circuit, it will show a slip pattern similar to that of a screw thread. A screw dislocation is much harder to visualize. Imagine cutting a crystal along a plane and slipping one half across the other by a lattice vector, the halves fitting back together without leaving a defect. The motion of a screw dislocation is also a result of shear stress. Still, the defect line movement is perpendicular to the direction of the stress and the atom displacement rather than parallel.
The pattern may be either left or right-handed. This requires that some of the atomic bonds are re-formed continuously so that the crystal has almost the same form after yielding that it had before.
Source: William D. Callister, David G. Rethwisch. Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction 9th Edition, Wiley; 9 edition (December 4, 2013), ISBN-13: 978-1118324578.