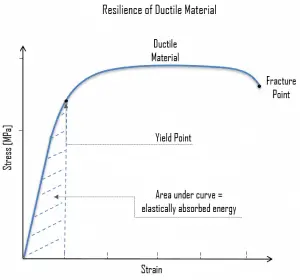
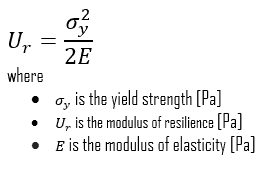 In materials science, resilience is a material’s ability and capacity to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically and then recover this amount of energy upon unloading. Proof resilience is known as the maximum energy that can be absorbed up to the elastic limit without creating a permanent deformation. The stress-strain curve is given by the area under the portion of a stress-strain curve (up to the yield point).
In materials science, resilience is a material’s ability and capacity to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically and then recover this amount of energy upon unloading. Proof resilience is known as the maximum energy that can be absorbed up to the elastic limit without creating a permanent deformation. The stress-strain curve is given by the area under the portion of a stress-strain curve (up to the yield point).
Under the assumption of linear elasticity or up to a proportional limit, resilience can be calculated by integrating the stress-strain curve from zero to the proportional limit.
The associated property is the modulus of resilience, Ur, defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed per unit volume without creating a permanent distortion. It is the strain energy per unit volume required to stress a material from an unloaded state up to the point of yielding. This analysis is not valid for non-linear elastic materials like rubber, for which the approach of the area under the curve till the elastic limit must be used.
Thus, resilient materials have high yield strengths and low moduli of elasticity. Such alloys are used in spring applications. The energy expended in deforming the spring is stored and can be recovered when it returns to its original shape.