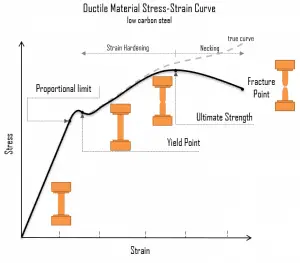
One of the stages in the stress-strain curve is the strain hardening region. This region starts as the strain goes beyond the yield point and ends at the ultimate strength point, the maximal stress shown in the stress-strain curve. In this region, the stress mainly increases as the material elongates, except that there is a nearly flat region at the beginning. Strain hardening is also called work-hardening or cold-working. It is called cold-working because the plastic deformation must occur at a temperature low enough that atoms cannot rearrange themselves. It is a process of making a metal harder and stronger through plastic deformation. When a metal is plastically deformed, dislocations move, and additional dislocations are generated. Dislocations can move if the atoms from one of the surrounding planes break their bonds and rebond with the atoms at the terminating edge. The dislocation density in a metal increases with deformation or cold work because of dislocation multiplication or the formation of new dislocations. The more dislocations within a material, the more they interact and become pinned or tangled. This will result in a decrease in the mobility of the dislocations and a strengthening of the material.