Source: wikipedia.org
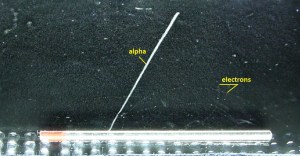
Cloud chambers, also known as Wilson cloud chambers, are particle detectors essential devices in early nuclear and particle physics research. Cloud chambers, one of the most simple instruments to study elementary particles, have been substituted by more modern detectors in actual research, but they remain a very interesting pedagogical apparatus.
Expansion Cloud Chamber
The air inside the sealed device was saturated with water vapor in Wilson’s original chamber. Then a diaphragm was used to expand the air inside the chamber (adiabatic expansion), cooling the air and condensing water vapor. Hence the name expansion cloud chamber is used. The first antiparticle, the positron, the muon, and the first strange particle, the kaon, were identified using a cloud chamber.
Diffusion Cloud Chamber
Although diffusion cloud chambers were never broadly used in nuclear and particle physics research, being easy to build and carry, they remain interesting educational instruments. A diffusion cloud chamber differs from the expansion cloud chamber in that it is continuously sensitized to radiation. The bottom must be cooled to a rather low temperature, generally colder than −26 °C (−15 °F). Instead of water vapor, alcohol is used because of its lower freezing point. Nowadays, they are an easy way of learning about and visualizing elementary particles and radiation.