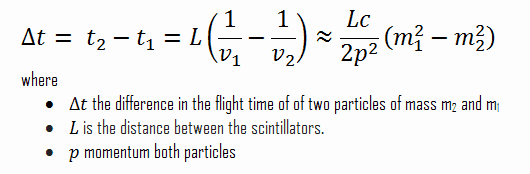Time of flight detectors (TOF) determine charged particle velocity by measuring the time required to travel from the interaction point to the time of flight detector or between two detectors. As was written, scintillation counters (especially with organic scintillators) can provide excellent time resolution. Therefore they can be used as a time of flight detector to discriminate between a lighter and a heavier elementary particle of the same momentum using their time of flight. The first of the scintillators activates a clock upon being hit, while the other stops the clock upon being hit. If the two masses are denoted by m1 and m2 and have velocities v1 and v2, then the time of flight difference is given by:
These detectors can also be used to measure the time of flight for reaching some scintillation counter located at a distance L from the point of origin of the particle to determine the velocity and, therefore, the particle’s rest mass; thus, they can be used for particle separation.
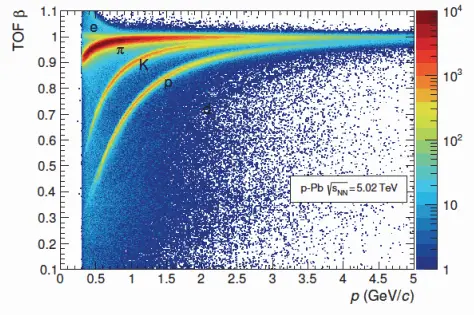
Source: Particle Detectors; Raffaella De Vita; INFN – Sezione di Genova