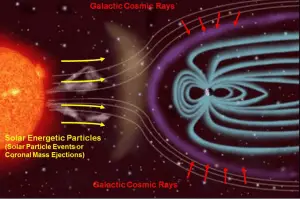
Solar cosmic radiation refers to sources of radiation in the form of high-energy particles (predominantly protons) emitted by the Sun, primarily in solar particle events (SPEs). The solar radiation incident in the upper atmosphere consists mostly of protons (99%), with energies below 100 MeV. Solar particle events, for example, occur when protons emitted by the Sun become accelerated either close to the Sun during a flare or in interplanetary space by coronal mass ejection shocks. Note that the Sun has an 11-year cycle, which culminates in a dramatic increase in the number and intensity of solar flares, especially during periods when there are numerous sunspots.
Solar radiation is a significant radiation hazard to spacecraft and astronauts. Also, it produces significant dose rates at high altitudes, but only the most energetic radiation contributes to doses at ground level. Note that anyone who had been on the Moon’s surface during a particularly violent solar eruption in 2005 would have received a lethal dose.