Radon is a colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of radium. All isotopes of radon are radioactive, but the two radon isotopes radon-222 and radon-220 are very important from radiation protection point of view.
Isotopes of Radon
-
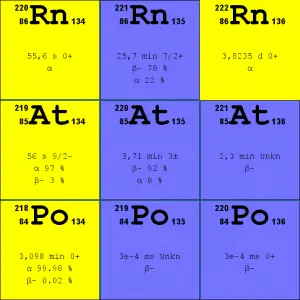
Source: JANIS (Java-based Nuclear Data Information Software); ENDF/B-VII.1 Radon-222. The radon-222 isotope is a natural decay product of the most stable uranium isotope (uranium-238). Thus it is a member of the uranium series. The half-life of radon-222 is 3.8 days, and it decays via alpha decay to polonium-218.
- Radon-220. The radon-220 isotope, commonly referred to as thoron, is a natural decay product of the most stable thorium isotope (thorium-232). Thus it is a member of the thorium series. The half-life of radon-220 is 55 seconds, and it decays via alpha decay to polonium-216.
It is important to note that radon is a noble gas, whereas all its decay products are metals. The main mechanism for radon entry into the atmosphere is diffusion through the soil. As a gas, radon diffuses through rocks and the soil. When radon disintegrates, the daughter metallic isotopes are ions that will be attached to other molecules like water and aerosol particles in the air. Therefore all discussions of radon concentrations in the environment refer to radon-222. While the average rate of production of radon-220 (thoron) is about the same as that of radon-222, the amount of radon-220 in the environment is much less than that of radon-222 because of the significantly shorter half-life (it has less time to diffuse) of radon-222 (55 seconds, versus 3.8 days respectively). Simply radon-220 has a lower chance of escaping from bedrock.
Radon-222
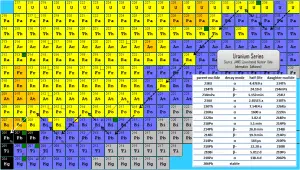
Radon-222 is a gas produced by the decay of radium-226. Both are a part of the natural uranium series. Since uranium is found in soil worldwide in varying concentrations, the dose of gaseous radon varies worldwide. Radon-222 is the most important and most stable isotope of radon. It has a half-life of only 3.8 days, making radon one of the rarest elements since it decays away quickly. An important source of natural radiation is radon gas, which seeps continuously from bedrock but can accumulate in poorly ventilated houses because of its high density. The fact radon is gas plays a crucial role in the spreading of all its daughter nuclei. Simply radon is a transport medium from bedrock to the atmosphere (or inside buildings) for its short-lived decay products (Pb-210 and Po-210), which posses much more health risks.