The Rankine cycle is often plotted on a pressure-volume diagram (pV diagram) and a temperature-entropy diagram (Ts diagram).
When plotted on a pressure-volume diagram, the isobaric processes follow the isobaric lines for the gas (the horizontal lines), adiabatic processes move between these horizontal lines, and the area bounded by the complete cycle path represents the total work that can be done during one cycle.
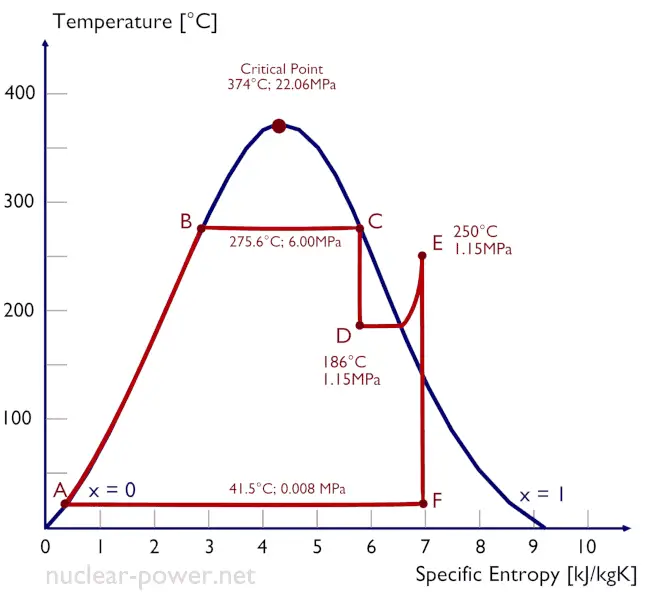
The temperature-entropy diagram (Ts diagram) in which the thermodynamic state is specified by a point on a graph with specific entropy (s) as the horizontal axis and absolute temperature (T) as the vertical axis. Ts diagrams are a useful and common tool, particularly because it helps to visualize the heat transfer during a process. For reversible (ideal) processes, the area under the T-s curve of a process is the heat transferred to the system during that process.