A polytropic process is any thermodynamic process that can be expressed by the following equation:
pVn = constant
The polytropic process can describe gas expansion and compression, which include heat transfer. The exponent n is known as the polytropic index, and it may take on any value from 0 to ∞, depending on the particular process.
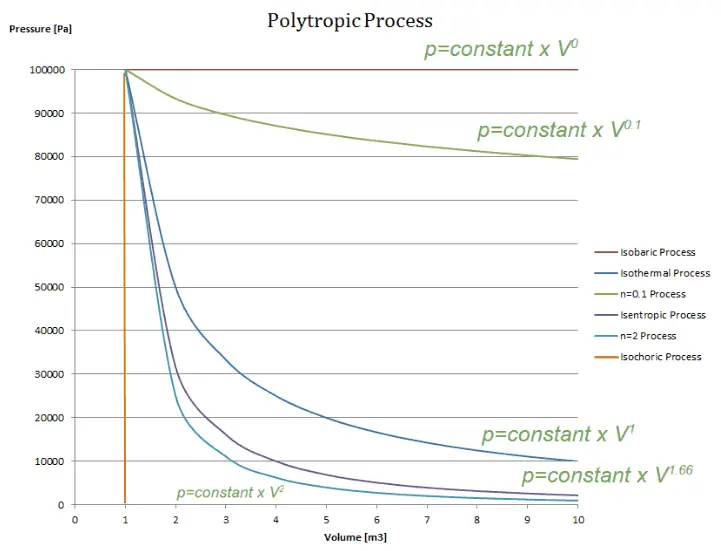
There are some special cases of n, which corresponds to particular processes:
- the case n = 0, p= constant, corresponds to an isobaric (constant-pressure) process.
- the case n = 1, pV = constant, corresponds to an isothermal (constant-temperature) process.
- the case n = , pV = constant, corresponds to an isentropic (constant-entropy) process.
- the case n ➝ ∞ corresponds to an isochoric (constant-volume) process.
- the case 1 < n < , in this process, heat and workflows, go in opposite directions, This process occurs, for example, in vapor compression refrigeration during compression
- the case < n < ∞, in this process, heat and workflows go in the same direction, This process occurs, for example, in an internal combustion engine (e.g.,, Otto cycle), in which there are heat losses through the cylinder walls during a gas expansion (power stroke).
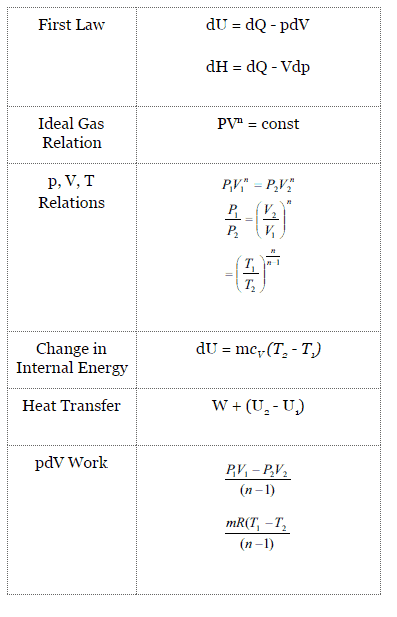
For a polytropic process between two states:
p1V1n = p2V2n