Energy is generally defined as the potential to do work or produce heat. This definition causes the SI unit for energy to be the same as the unit of work – the joule (J). Joule is a derived unit of energy, and it is named in honor of James Prescott Joule and his experiments on the mechanical equivalent of heat. In more fundamental terms, 1 joule is equal to:
1 J = 1 kg.m2/s2
Since energy is a fundamental physical quantity and is used in various physical and engineering branches, there are many energy units in physics and engineering.
British Thermal Unit (unit: BTU)
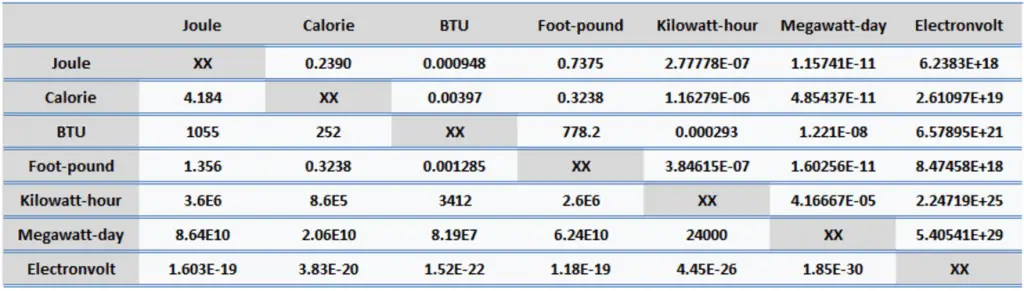
British Thermal Unit (unit: BTU). British Thermal Unit is a traditional unit of heat. It is part of the British Imperial system of units. It is defined as the amount of heat that must be absorbed by 1 pound of water to raise its temperature by 1 °F at the temperature that water has its greatest density (approximately 39 degrees Fahrenheit). Its counterpart in the International System of Units (SI) is the calorie, defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius.
-
- 1 British Thermal Unit (BTU) = 1055 J
- 1 British Thermal Unit (BTU) = 252 calories
- 1 British Thermal Unit (BTU) = 0.000293 kWh