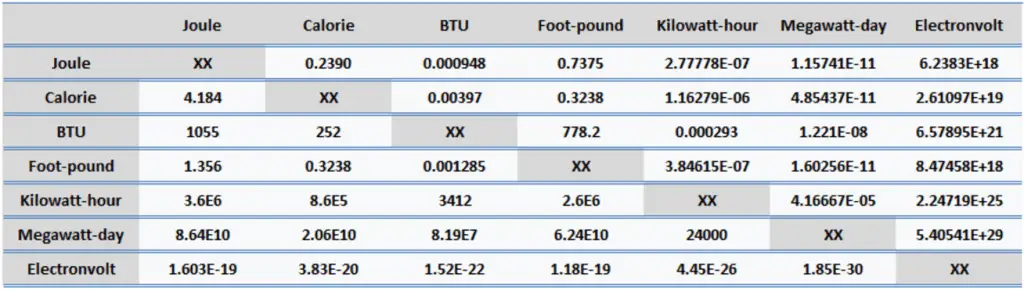
Energy is generally defined as the potential to do work or produce heat. This definition causes the SI unit for energy to be the same as the unit of work – the joule (J). Joule is a derived unit of energy, and it is named in honor of James Prescott Joule and his experiments on the mechanical equivalent of heat. In more fundamental terms, 1 joule is equal to:
1 J = 1 kg.m2/s2
Since energy is a fundamental physical quantity and is used in various physical and engineering branches, there are many energy units in physics and engineering.
Electronvolt (unit: eV)
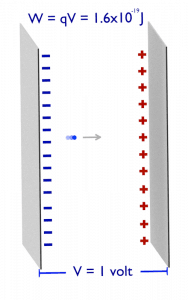
Electronvolt (unit: eV). Electronvolts are a traditional unit of energy, particularly in atomic and nuclear physics. An electronvolt is equal to the energy gained by a single electron when accelerated through 1 volt of electric potential difference. The work done on the charge is given by the charge times the voltage difference, therefore the work W on electron is: W = qV = (1.6 x 10-19 C) x (1 J/C) = 1.6 x 10-19 J. Since this is a very small unit, it is more convenient to use multiples of electronvolts: kilo-electronvolts (keV), mega-electronvolts (MeV), giga-electronvolts (GeV), and so on. Since Albert Einstein showed that mass and energy are equivalent and convertible one into the other, the electronvolt is also a unit of mass. It is common in particle physics, where units of mass and energy are often interchanged, to express mass in units of eV/c2, where c is the speed of light in a vacuum (from E = mc2). For example, it can be said the proton has a mass of 938.3 MeV, although strictly speaking, it should be 938.3 MeV/c2. For example, an electron-positron annihilation occurs when a negatively charged electron and a positively charged positron (each with a mass of 0.511 MeV/c2) collide. When an electron and a positron collide, they annihilate, resulting in the complete conversion of their rest mass to pure energy (according to the E=mc2 formula) in the form of two oppositely directed 0.511 MeV gamma rays (photons).
e− + e+ → γ + γ (2x 0.511 MeV)
-
- 1 eV = 1.603 x 10-19 J
- 1 eV = 3.83 x 10-20 cal
- 1 eV = 1.52 x 10-22 BTU
Example of Energies in Electronvolts
- Thermal neutrons are neutrons in thermal equilibrium with a surrounding medium of the temperature of 290K (17 °C or 62 °F). Most probable energy at 17°C (62°F) for Maxwellian distribution is 0.025 eV (~2 km/s).
- The thermal energy of a molecule is at room temperature, about 0.04 eV.
- Approximately 1 eV corresponds to an infrared photon of wavelength 1240 nm.
- Visible light photons have energies in range 1.65 eV (red) – 3.26 eV (violet).
- The first resonance in n + 238U reaction is at 6.67 eV (energy of incident neutron), which corresponds to the first virtual level in 239U, which has a total width of only 0.027 eV mean life of this state is 2.4×10-14s.
- The ionization energy of atomic hydrogen is 13.6 eV.
- Carbon-14 decays into nitrogen-14 through beta decay (pure beta decay). The emitted beta particles have a maximum energy of 156 keV, while their weighted mean energy is 49 keV.
- High energy diagnostic medical x-ray photons have kinetic energies of about 200 keV.
- Thallium 208, one of the nuclides in the 232U decay chain, emits gamma rays of 2.6 MeV, which are very energetic and highly penetrating.
- The typical kinetic energy of alpha particle from radioactive decay is about 5 MeV. It is caused by the mechanism of their production.
- The total energy released in a reactor is about 210 MeV per 235U fission, distributed as shown in the table. In a reactor, the average recoverable energy per fission is about 200 MeV, being the total energy minus the energy of antineutrinos that are radiated away.
- Cosmic rays can have energies of 1 MeV – 1000 TeV.