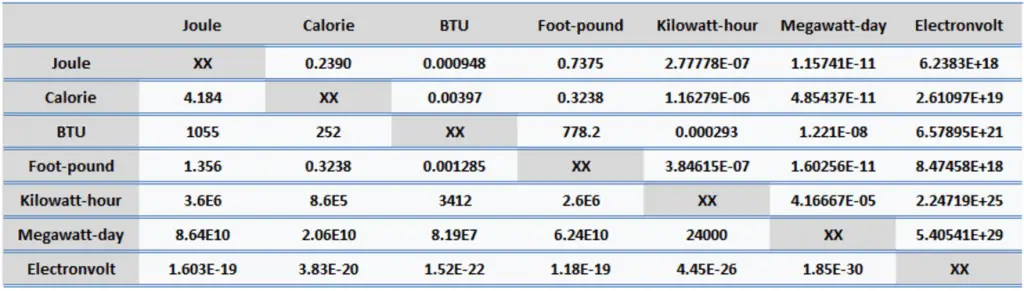
Energy is generally defined as the potential to do work or produce heat. This definition causes the SI unit for energy to be the same as the unit of work – the joule (J). Joule is a derived unit of energy, and it is named in honor of James Prescott Joule and his experiments on the mechanical equivalent of heat. In more fundamental terms, 1 joule is equal to:
1 J = 1 kg.m2/s2
Since energy is a fundamental physical quantity and is used in various physical and engineering branches, there are many energy units in physics and engineering.
Foot-pound force (unit: ft.lbf)
Foot-pound force (unit: ft.lbf). Foot-pound force is a derived unit of work and energy. It is equal to the energy transferred to an object when a force of one pound-force (lbf) acts on that object in the direction of its motion through a distance of one foot. The corresponding SI unit is the joule. The foot-pound is often used in ballistics, especially in the United States. Typically muzzle energies of bullets are given in foot-pound force.
-
- 1 foot-pound force = 1.356 J
- 1 foot-pound force = 0.324 cal
- 1 foot-pound force = 0.00129 BTU