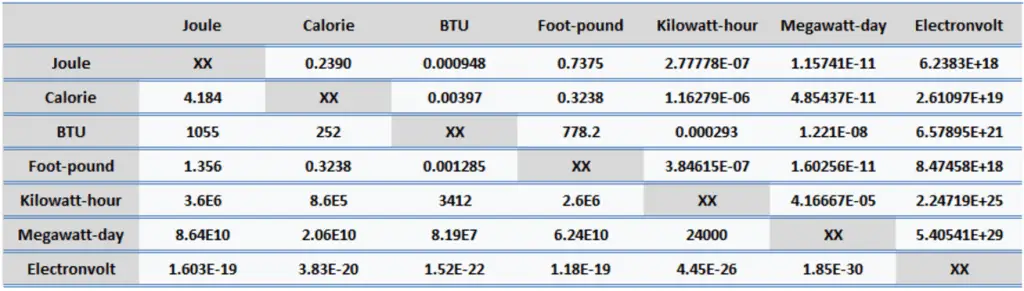
Energy is generally defined as the potential to do work or produce heat. This definition causes the SI unit for energy to be the same as the unit of work – the joule (J). Joule is a derived unit of energy, and it is named in honor of James Prescott Joule and his experiments on the mechanical equivalent of heat. In more fundamental terms, 1 joule is equal to:
1 J = 1 kg.m2/s2
Since energy is a fundamental physical quantity and is used in various physical and engineering branches, there are many energy units in physics and engineering.
Kilowatt-hour (unit: kWh)
Kilowatt-hour (unit: kWh). Kilowatt-hour is a derived unit of energy. It is used to measure energy, especially electrical energy in commercial applications. One kilowatt-hour equals one kilowatt of power produced or consumed for one hour (kilowatts multiplied by the time in hours). Electric utilities commonly use the kilowatt-hour as a billing unit for energy delivered to consumers. 1kW . h = 1kW . 3600s = 3600kWs = 3600kJ = 3600000J. One kilowatt-hour corresponds to the heat required to evaporate 1.58 kg of liquid water at 100°C. A 100-watt radio that operates for 10 hours continuously consumes one kilowatt-hour.
-
- 1 kWh = 3.6 x 106 J
- 1 kWh = 8.6 x 105 cal
- 1 kWh = 3412 BTU