Enthalpy in Intensive Units – Specific Enthalpy
The enthalpy can be made into an intensive or specific variable by dividing by the mass. Engineers use the specific enthalpy in thermodynamic analysis more than the enthalpy itself. The specific enthalpy (h) of a substance is its enthalpy per unit mass. It equals the total enthalpy (H) divided by the total mass (m).
h = H/m
where:
h = specific enthalpy (J/kg)
H = enthalpy (J)
m = mass (kg)
Note that enthalpy is the thermodynamic quantity equivalent to the total heat content of a system. The specific enthalpy is equal to the specific internal energy of the system plus the product of pressure and specific volume.
h = u + pv
In general, enthalpy is a property of a substance, like pressure, temperature, and volume, but it cannot be measured directly. Normally, the enthalpy of a substance is given for some reference value. For example, the specific enthalpy of water or steam is given using the reference that the specific enthalpy of water is zero at 0.01°C and normal atmospheric pressure, where hL = 0.00 kJ/kg. The absolute value of specific enthalpy is unknown is not a problem, however, because it is the change in specific enthalpy (∆h) and not the absolute value that is important in practical problems.
Specific Enthalpy of Wet Steam
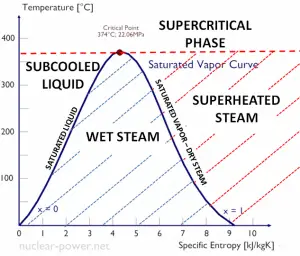 The specific enthalpy of saturated liquid water (x=0) and dry steam (x=1) can be picked from steam tables. In the case of wet steam, the actual enthalpy can be calculated with the vapor quality, x, and the specific enthalpies of saturated liquid water and dry steam:
The specific enthalpy of saturated liquid water (x=0) and dry steam (x=1) can be picked from steam tables. In the case of wet steam, the actual enthalpy can be calculated with the vapor quality, x, and the specific enthalpies of saturated liquid water and dry steam:
hwet = hs x + (1 – x ) hl
where
hwet = enthalpy of wet steam (J/kg)
hs = enthalpy of “dry” steam (J/kg)
hl = enthalpy of saturated liquid water (J/kg)
As can be seen, wet steam will always have lower enthalpy than dry steam.
Example:
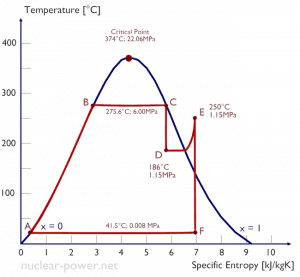
A high-pressure steam turbine stage operates at a steady state with inlet conditions of 6 MPa, t = 275.6°C, x = 1 (point C). Steam leaves this turbine stage at a pressure of 1.15 MPa, 186°C, and x = 0.87 (point D). Calculate the enthalpy difference between these two states.
The enthalpy for the state C can be picked directly from steam tables, whereas the enthalpy for the state D must be calculated using vapor quality:
h1, wet = 2785 kJ/kg
h2, wet = h2,s x + (1 – x ) h2,l = 2782 . 0.87 + (1 – 0.87) . 790 = 2420 + 103 = 2523 kJ/kg
Δh = 262 kJ/kg