 Most of PWRs use uranium fuel, which is in the form of uranium dioxide. Uranium dioxide is a black semiconducting solid with very low thermal conductivity. On the other hand, uranium dioxide has a very high melting point and has well-known behavior. The UO2 is pressed into pellets, and these pellets are then sintered into the solid.
Most of PWRs use uranium fuel, which is in the form of uranium dioxide. Uranium dioxide is a black semiconducting solid with very low thermal conductivity. On the other hand, uranium dioxide has a very high melting point and has well-known behavior. The UO2 is pressed into pellets, and these pellets are then sintered into the solid.
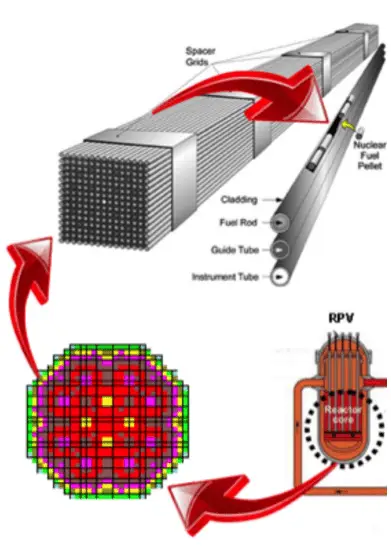
These pellets are then loaded and encapsulated within a fuel rod (or fuel pin) made of zirconium alloys due to their very low absorption cross-section (unlike stainless steel). The surface of the tube, which covers the pellets, is called fuel cladding. The collection of fuel rods or elements is called the fuel assembly. The fuel assembly constitutes the base element of the nuclear reactor core. The reactor core (PWR type) contains about 157 fuel assemblies (depending on a reactor type). Western PWRs use a square lattice arrangement, and assemblies are characterized by the number of rods they contain, typically 17×17 in current designs. The enrichment of fuel rods is never uniform. The enrichment is differentiated in the radial direction but also axial direction. This arrangement significantly influences the power distribution.
Russian VVER-type reactors use a fuel that is characterized by their hexagonal arrangement, but is otherwise of similar length and structure to other PWR fuel assemblies.