Classification of Turbines – steam supply and exhaust conditions
Steam turbines may be classified into different categories depending on their purpose and working pressures. The industrial usage of a turbine influences the initial and final conditions of steam. A pressure difference must exist between the steam supply and the exhaust for any steam turbine to operate.
This classification includes:
- Condensing Steam Turbine,
- Back-pressure Steam Turbine,
- Reheat Steam Turbine,
- Turbine with Steam Extraction
Back-pressure Steam Turbine
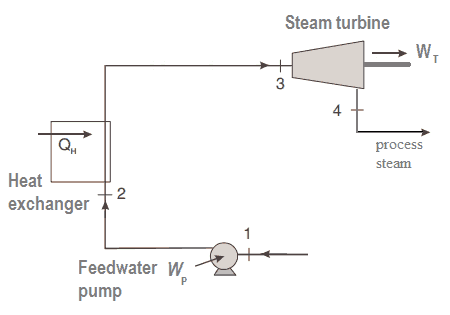
Back-pressure steam turbines or non-condensing turbines are most widely used for process steam applications. Steam is a principal energy source for many industrial processes. The popularity of process steam as an energy source stems from its many advantages, which include:
- high heat capacity,
- transportability
- low toxicity
The process steam can be produced by back-pressure steam turbines, which also generate mechanical work (or electrical energy). Back-pressure turbines expand the live steam supplied by the boiler to the pressure at which the steam is required for the process. A regulating valve controls the exhaust pressure to suit the needs of the process steam pressure. Back-pressure turbines are commonly found at refineries, district heating units, pulp and paper plants, and desalination facilities where large amounts of low-pressure process steam are needed. The electric power generated by the back-pressure turbine is directly proportional to the amount of process steam required.