The most important turbine elements are the turbine blades. They are the principal elements that convert the pressure energy of working fluid into kinetic energy. Turbine blades are of two basic types:
- moving blades
- fixed blades
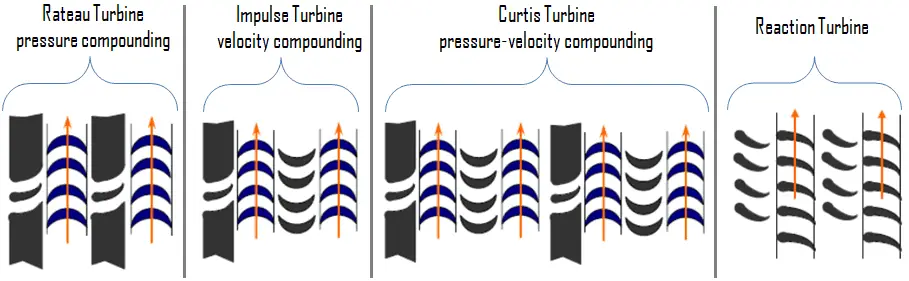
 In steam turbines, the steam expands through the fixed blade (nozzle), where the pressure potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. The high-velocity steam from fixed nozzles impacts the moving blades, then changes its direction and also expands (in the case of reaction type blades). The change in its direction and the steam acceleration (in the case of reaction type blades) applies a force. The resulting impulse drives the blades forward, causing the rotor to turn. Steam turbine types based on blade geometry and energy conversion process are:
In steam turbines, the steam expands through the fixed blade (nozzle), where the pressure potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. The high-velocity steam from fixed nozzles impacts the moving blades, then changes its direction and also expands (in the case of reaction type blades). The change in its direction and the steam acceleration (in the case of reaction type blades) applies a force. The resulting impulse drives the blades forward, causing the rotor to turn. Steam turbine types based on blade geometry and energy conversion process are:
- impulse turbine
- reaction turbine
Modern steam turbines frequently employ both reaction and impulse in the same unit, varying the degree of reaction and impulse from the blade root to its periphery. The rotor blades are usually designed like an impulse blade at the rot and a reaction blade at the tip.
 The efficiency and reliability of a turbine depend on the proper design of the blades. It is, therefore, necessary for all engineers involved in turbines engineering to have an overview of the importance and the basic design aspects of the steam turbine blades. The engineering of turbine blades is a multi-disciplinary task. It involves thermodynamics, aerodynamics, mechanical and material engineering.
The efficiency and reliability of a turbine depend on the proper design of the blades. It is, therefore, necessary for all engineers involved in turbines engineering to have an overview of the importance and the basic design aspects of the steam turbine blades. The engineering of turbine blades is a multi-disciplinary task. It involves thermodynamics, aerodynamics, mechanical and material engineering.
For gas turbines, the turbine blades are often the limiting component. The highest temperature in the cycle occurs at the end of the combustion process, and it is limited by the maximum temperature that the turbine blades can withstand. As usual, metallurgical considerations (about 1700 K) place upper limits on thermal efficiency. Therefore turbine blades often use exotic materials like superalloys and different cooling methods, such as internal air channels, boundary layer cooling, and thermal barrier coatings. The development of superalloys in the 1940s and new processing methods such as vacuum induction melting in the 1950s greatly increased the temperature capability of turbine blades. Modern turbine blades often use nickel-based superalloys that incorporate chromium, cobalt, and rhenium.
Steam turbine blades are not exposed to such high temperatures, but they must withstand an operation with two-phase fluid. A high content of water droplets can cause rapid impingement and erosion of the blades, which occurs when condensed water is blasted onto the blades. For example, condensate drains are installed in the steam piping leading to the turbine to prevent this. Another challenge for engineers is the design of blades of the last stage of the LP turbine. These blades must be (due to high specific volume of steam) very long, which induces enormous centrifugal forces during operation. Therefore, turbine blades are subjected to stress from centrifugal force (turbine stages can rotate at tens of thousands of revolutions per minute (RPM), but usually at 1800 RPM) and fluid forces that can cause a fracture, yielding, or creep failures.
See also: Materials for Steam Turbines
Turbine Blades – Root, Profile, Shroud
Turbine blades are usually divided into three parts:
- Root. The root is a constructional feature of turbine blades, which fixes the blade into the turbine rotor.
- Profile. The profile converts the kinetic energy of steam into the mechanical energy of the blade.
- Shroud. The shroud reduces the blade’s vibration, which can be induced by the flowing of high pressure steam through the blades.
Types of Steam Turbines
Steam turbines may be classified into different categories depending on their construction, working pressures, size, and other parameters. But there are two basic types of steam turbines:
- impulse turbines
- reaction turbines.
The main distinction is how the steam is expanded as it passes through the turbine.
Impulse Turbine and Reaction Turbine
Steam turbine types based on blade geometry and energy conversion process are impulse turbine and reaction turbine.