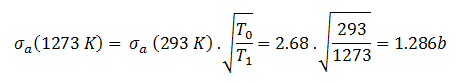
Source: JANIS 4.0
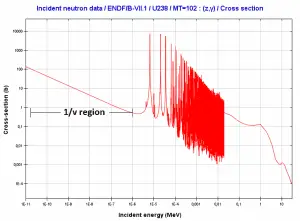
For thermal neutrons (in 1/v region), the absorption cross-section increases as the neutron’s velocity (kinetic energy) decrease. Therefore the 1/v law can determine the shift in absorption cross-section if the neutron is in equilibrium with a surrounding medium. This phenomenon is because the nuclear force between the target nucleus and the neutron has a longer time to interact.
This law is applicable only for absorption cross-section and only in the 1/v region.
Example of cross-sections in 1/v region:
The absorbtion cross-section for 238U at 20°C = 293K (~0.0253 eV) is:
.
The absorbtion cross-section for 238U at 1000°C = 1273K is equal to:
This cross-section reduction is caused only due to the shift of temperature of surrounding medium.