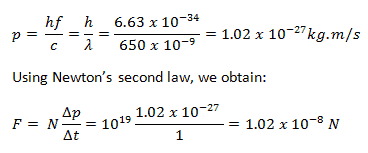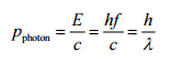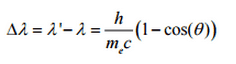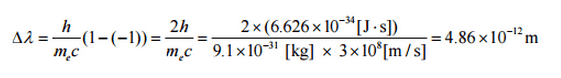The modern photon concept was developed (1905) by Albert Einstein to explain the photoelectric effect, in which he proposed the existence of discrete energy packets during the transmission of light.
Before Albert Einstein, notably the German physicist Max Planck had prepared the way for the concept by explaining that objects that emit and absorb light do so only in amounts of energy that are quantized, that means every change of energy can occur only by certain particular discrete amounts and the object cannot change the energy in any arbitrary way. The concept of the modern photon came into general use after the physicist Arthur H. Compton demonstrated (1923) the corpuscular nature of X-rays. This was the validation of Einstein’s hypothesis that light itself is quantized.
The term photon comes from Greek phōtos, “light,” and a photon is usually denoted by the symbol γ (gamma). The photons are also symbolized by hν (in chemistry and optical engineering), where h is Planck’s constant and the Greek letter ν (nu) is the photon’s frequency. The radiation frequency is the key parameter of all photons because it determines the energy of a photon. Photons are categorized according to the energies from low-energy radio waves and infrared radiation, through visible light, to high-energy X-rays and gamma rays.
Momentum of Photon
A photon, the quantum of electromagnetic radiation, is an elementary particle, the force carrier of the electromagnetic force. The modern photon concept was developed (1905) by Albert Einstein to explain the photoelectric effect, in which he proposed the existence of discrete energy packets during the transmission of light.
In 1916, Einstein extended his concept of light quanta (photons) by proposing that a quantum of light has linear momentum. Although a photon is massless, it has momentum, which is related to its energy E, frequency f, and wavelength by:
Thus, when a photon interacts with another object, energy and momentum are transferred, as if there were a collision between the photon and matter in the classical sense.
The momentum of a Photon – Compton Scattering
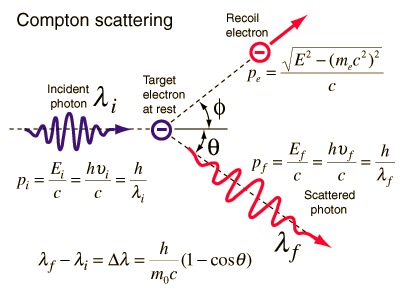
Source: hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu
The Compton formula was published in 1923 in the Physical Review. Compton explained that the particle-like momentum of photons causes the X-ray shift. Compton scattering formula is the mathematical relationship between the shift in wavelength and the scattering angle of the X-rays. In the case of Compton scattering, the photon of frequency f collides with an electron at rest. The photon bounces off the electron upon collision, giving up some of its initial energy (given by Planck’s formula E=hf). While the electron gains momentum (mass x velocity), the photon cannot lower its velocity. As a result of momentum conservation law, the photon must lower its momentum given by:
So the decrease in photon’s momentum must be translated into a decrease in frequency (increase in wavelength Δλ = λ’ – λ). The shift of the wavelength increased with scattering angle according to the Compton formula:
where λ is the initial wavelength of photon λ’ is the wavelength after scattering, h is the Planck constant = 6.626 x 10-34 J.s, me is the electron rest mass (0.511 MeV)c is the speed of light Θ is the scattering angle. The minimum change in wavelength (λ′ − λ) for the photon occurs when Θ = 0° (cos(Θ)=1) and is at least zero. The maximum change in wavelength (λ′ − λ) for the photon occurs when Θ = 180° (cos(Θ)=-1). In this case, the photon transfers to the electron as much momentum as possible. The maximum change in wavelength can be derived from the Compton formula:
The quantity h/mec is known as the Compton wavelength of the electron and is equal to 2.43×10−12 m.