Key features of gamma rays are summarized in the following few points:
- Gamma rays are high-energy photons (about 10 000 times as much energy as the visible photons),
- The same photons as the photons forming the visible range of the electromagnetic spectrum – light.
- Photons (gamma rays and X-rays) can ionize atoms directly (despite they are electrically neutral) through the Photoelectric effect and the Compton effect, but secondary (indirect) ionization is much more significant.
- Gamma rays ionize matter primarily via indirect ionization.
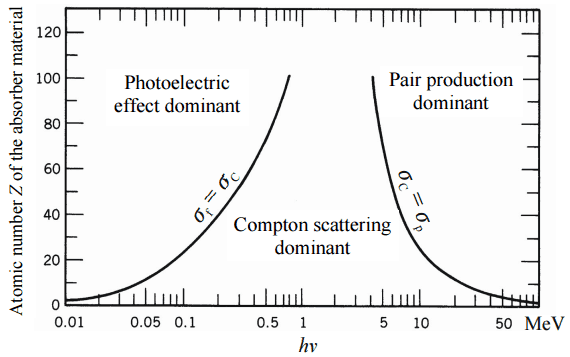
- Although many possible interactions are known, there are three key interaction mechanisms with the matter.
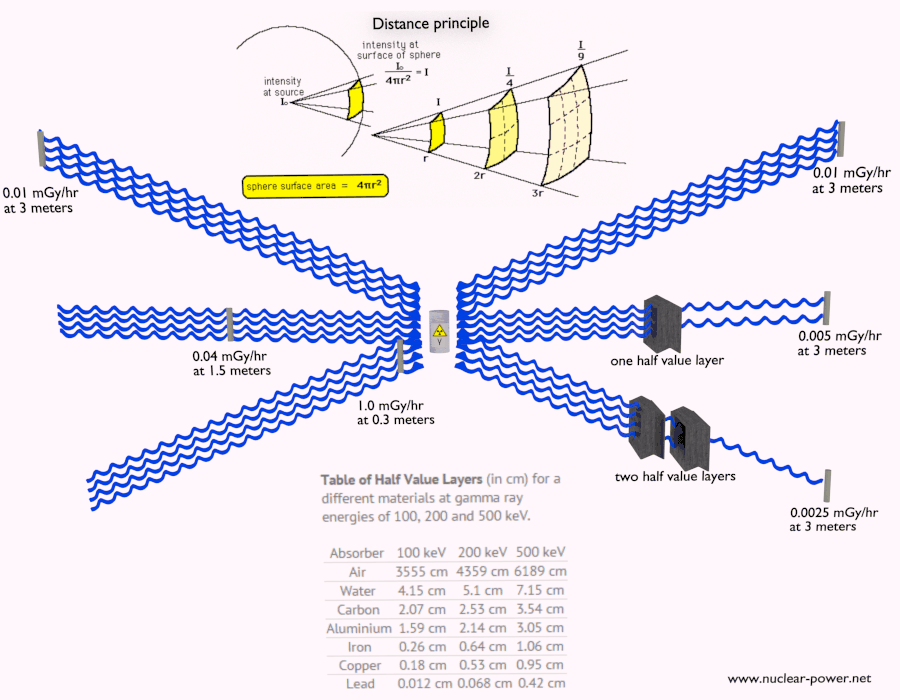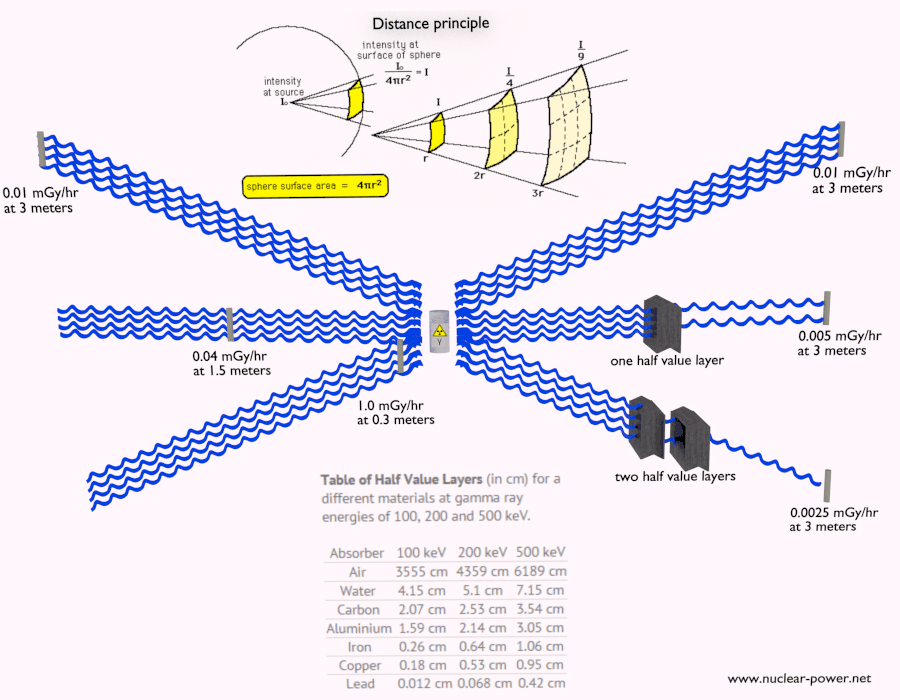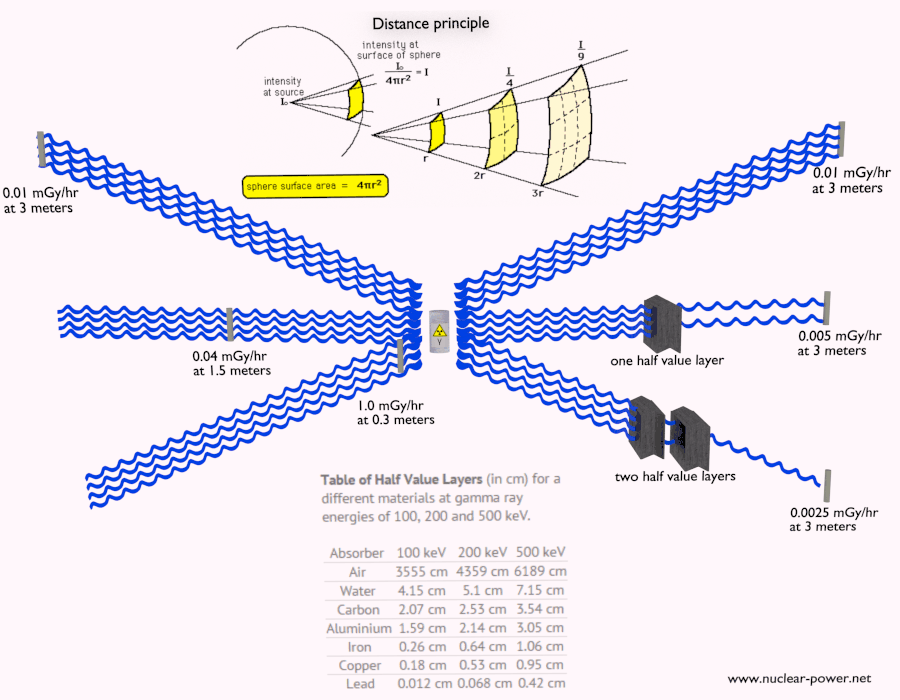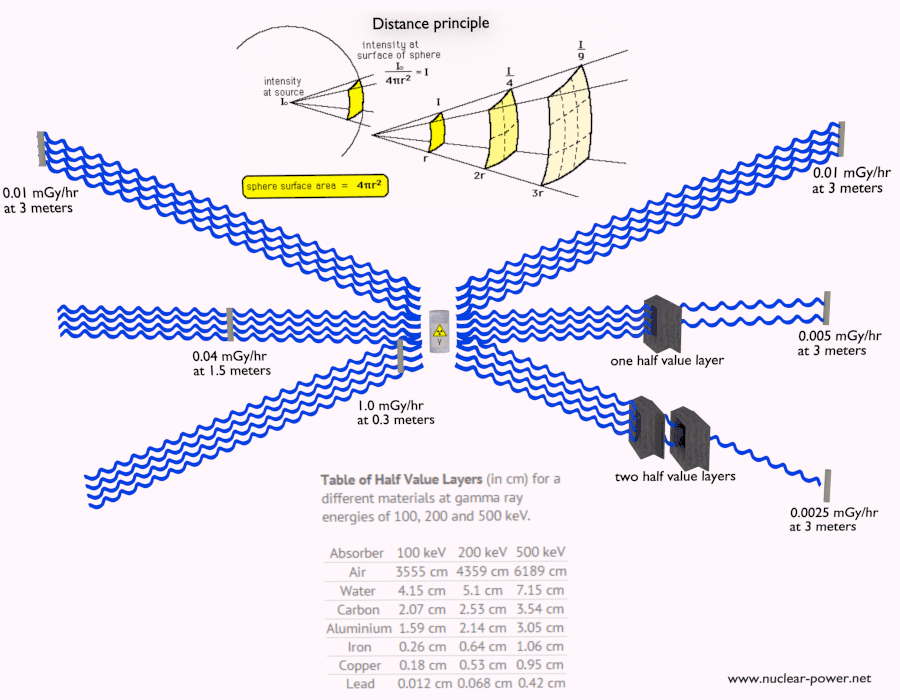
- Gamma rays travel at the speed of light, and they can travel thousands of meters in the air before spending their energy.
- Since gamma radiation is very penetrating, it must be shielded by very dense materials, such as lead or uranium.
- The distinction between X-rays and gamma rays is not so simple and has changed in recent decades. According to the currently valid definition, X-rays are emitted by electrons outside the nucleus, while the nucleus emits gamma rays.
- Gamma rays frequently accompany the emission of alpha and beta radiation.

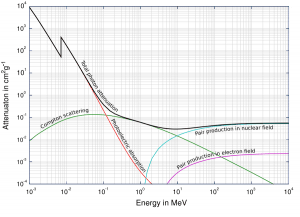
Source: Wikimedia Commons