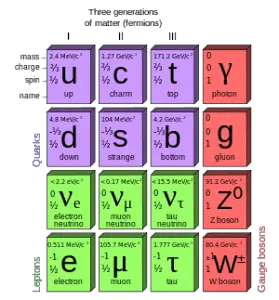
 The most familiar baryons are the proton and neutron, each constructed from up and down quarks.
The most familiar baryons are the proton and neutron, each constructed from up and down quarks.
The proton has a quark composition of uud, and so its charge quantum number is:
q(uud) = 2/3 + 2/3 + (-1/3) = +1
The neutron has a quark composition of udd, and its charge quantum number is therefore:
q(udd) = 2/3 + (-1/3) + (-1/3) = 0
Since the neutron has no net electric charge, it is not affected by electric forces, but the neutron does have a slight distribution of electric charge within it. This is caused by by its internal quark structure. This results in non-zero magnetic moment (dipole moment) of the neutron. Therefore the neutron interacts also via electromagnetic interaction, but much weaker than the proton.