For a given event, the cross-section σ is given by
σ = μ/n
where
- σ is the cross-section of this event [m2],
- μ is the attenuation coefficient due to the occurrence of this event [m-1],
- n is the density of the target particles [m-3].
In nuclear physics, the nuclear cross section of a nucleus is commonly used to characterize the probability that a nuclear reaction will occur. The cross-section is typically denoted σ and measured in units of area [m2]. The standard unit for measuring a nuclear cross section is the barn, which is equal to 10−28 m² or 10−24 cm². It can be seen the concept of a nuclear cross section can be quantified physically in terms of “characteristic target area” where a larger area means a larger probability of interaction.
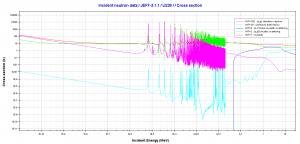
Source: JANIS (Java-based Nuclear Data Information Software); The JEFF-3.1.1 Nuclear Data Library
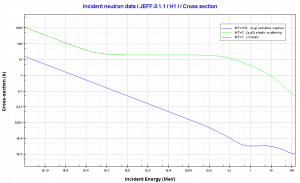 Hydrogen. Neutron absorption and scattering. Comparison of cross-sections.
Hydrogen. Neutron absorption and scattering. Comparison of cross-sections.
Source: JANIS (Java-based Nuclear Data Information Software); The JEFF-3.1.1 Nuclear Data Library