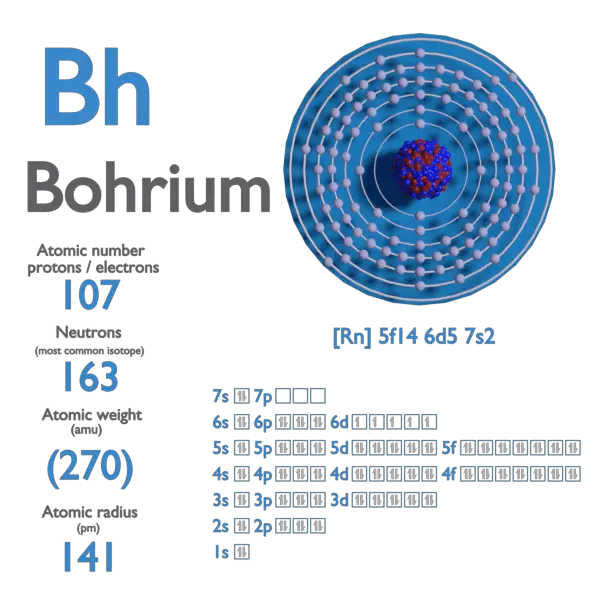
Electron Affinity and Electronegativity of Bohrium
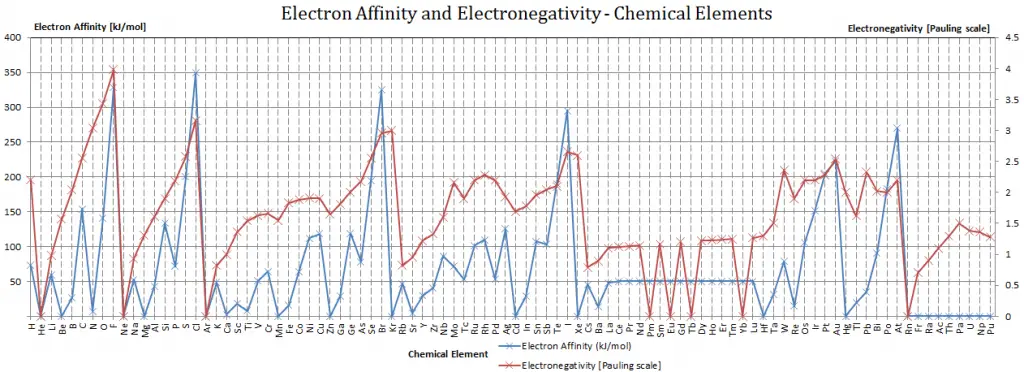
Electron Affinity of Bohrium is — kJ/mol.
Electronegativity of Bohrium is —.
First Ionization Energy of Bohrium is — eV.
Electron Affinity
In chemistry and atomic physics, the electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as:
the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom or molecule (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative ion.
X + e– → X– + energy Affinity = – ∆H
In other words, it can be expressed as the neutral atom’s likelihood of gaining an electron. Note that ionization energies measure the tendency of a neutral atom to resist the loss of electrons. Electron affinities are more difficult to measure than ionization energies.
An atom of Bohrium in the gas phase, for example, gives off energy when it gains an electron to form an ion of Bohrium.
Bh + e– → Bh– – ∆H = Affinity = — kJ/mol
Electron affinity is one of the most important parameters that guide chemical reactivity. Molecules with high electron affinity form very stable negative ions which are important in the chemical and health industry as they purify the air, lift mood, and most importantly, act as strong oxidizing agents. To use electron affinities properly, it is essential to keep track of signs. When an electron is added to a neutral atom, energy is released. This affinity is known as the first electron affinity, and these energies are negative. By convention, the negative sign shows a release of energy. However, more energy is required to add an electron to a negative ion which overwhelms any release of energy from the electron attachment process. This affinity is known as the second electron affinity, and these energies are positive.
Halogens have the highest electron affinities among all elements. In fact, the electron affinity of Cl, 3.62 eV is the largest of all the elements. Superhalogens are molecules that have electron affinities (EA) greater than that of Cl, the element with the highest EA (3.62 eV).
It is well known that noble gases have closed electronic shell structure and hence have high ionization potentials and low electron affinities, due to which they are chemically inert and resistant to salt formation under most conditions.
Affinities of Nonmetals vs. Affinities of Metals
- Metals: Metals like to lose valence electrons to form cations to have a fully stable shell. The electron affinity of metals is lower than that of nonmetals. Mercury most weakly attracts an extra electron.
- Nonmetals: Generally, nonmetals have more positive electron affinity than metals. Nonmetals like to gain electrons to form anions to have a fully stable electron shell. Chlorine most strongly attracts extra electrons. The electron affinities of the noble gases have not been conclusively measured, so they may or may not have slightly negative values.
Learn more about electron affinities.
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards this atom. For this purpose, a dimensionless quantity, the Pauling scale, symbol χ, is the most commonly used.
The electronegativity of Bohrium is:
χ = —
In general, an atom’s electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it.
As it is usually calculated, electronegativity is not a property of an atom alone, but rather a property of an atom in a molecule. Even so, the electronegativity of an atom is strongly correlated with the first ionization energy, and negatively correlated with the electron affinity. Electrons with low ionization energies have low electronegativities because their nuclei do not exert a strong attractive force on electrons. Elements with high ionization energies have high electronegativities due to the strong pull exerted by the positive nucleus on the negative electrons. Therefore the electronegativity is greatest at the top-right of the periodic table and decreases toward the bottom-left.
Caesium is the least electronegative element (0.79); fluorine is the most (3.98).
Learn more about electronegativities.
First Ionization Energy of Bohrium
First Ionization Energy of Bohrium is — eV.
Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom.
X + energy → X+ + e−
where X is any atom or molecule capable of being ionized, X+ is that atom or molecule with an electron removed (positive ion), and e− is the removed electron.
A Bohrium atom, for example, requires the following ionization energy to remove the outermost electron.
Bh + IE → Bh+ + e− IE = — eV
The ionization energy associated with removal of the first electron is most commonly used. The nth ionization energy refers to the amount of energy required to remove an electron from the species with a charge of (n-1).
1st ionization energy
X → X+ + e−
2nd ionization energy
X+ → X2+ + e−
3rd ionization energy
X2+ → X3+ + e−
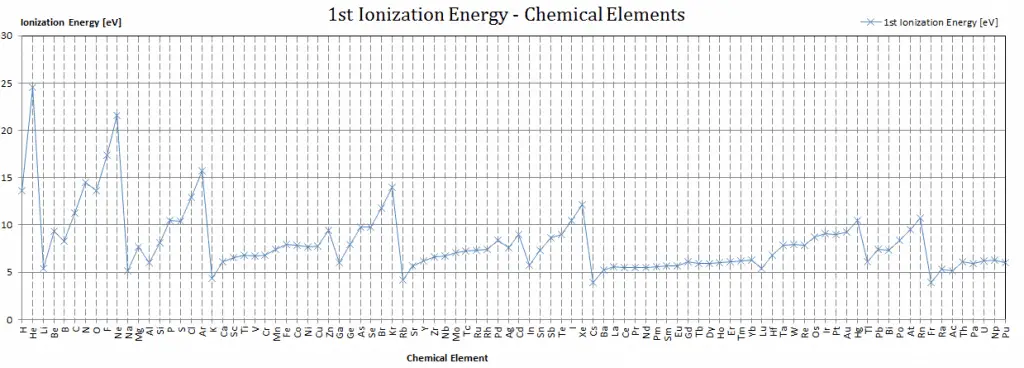
Ionization Energy for different Elements
There is ionization energy for each successive electron removed. The electrons that circle the nucleus move in fairly well-defined orbits. Some of these electrons are more tightly bound in the atom than others. For example, only 7.38 eV is required to remove the outermost electron from a lead atom, while 88,000 eV is required to remove the innermost electron. Helps to understand the reactivity of elements (especially metals, which lose electrons).
In general, the ionization energy increases moving up a group and moving left to right across a period. Moreover:
- Ionization energy is lowest for the alkali metals which have a single electron outside a closed shell.
- Ionization energy increases across a row on the periodic maximum for the noble gases which have closed shells.
For example, sodium requires only 496 kJ/mol or 5.14 eV/atom to ionize it. On the other hand neon, the noble gas, immediately preceding it in the periodic table, requires 2081 kJ/mol or 21.56 eV/atom.
Learn more about ionization energy.
Bohrium – Properties
| Element | Bohrium |
|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 107 |
| Symbol | Bh |
| Element Category | Transition Metal |
| Phase at STP | Synthetic |
| Atomic Mass [amu] | 264 |
| Density at STP [g/cm3] | — |
| Electron Configuration | [Rn] 5f14 6d5 7s2 |
| Possible Oxidation States | — |
| Electron Affinity [kJ/mol] | — |
| Electronegativity [Pauling scale] | — |
| 1st Ionization Energy [eV] | — |
| Year of Discovery | 1976 |
| Discoverer | Scientists at Dubna, Russia |
| Thermal properties | |
| Melting Point [Celsius scale] | — |
| Boiling Point [Celsius scale] | — |
| Thermal Conductivity [W/m K] | — |
| Specific Heat [J/g K] | — |
| Heat of Fusion [kJ/mol] | — |
| Heat of Vaporization [kJ/mol] | — |
Bohrium in Periodic Table
–
–
–