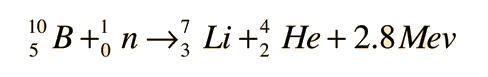Notation of nuclear reactions
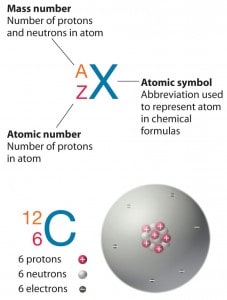
Standard nuclear notation shows (see picture) the chemical symbol, the mass number and the atomic number of the isotope.
If the initial nuclei are denoted by a and b, and the product nuclei are denoted by c and d, the reaction can be represented by the equation:
a + b → c + d
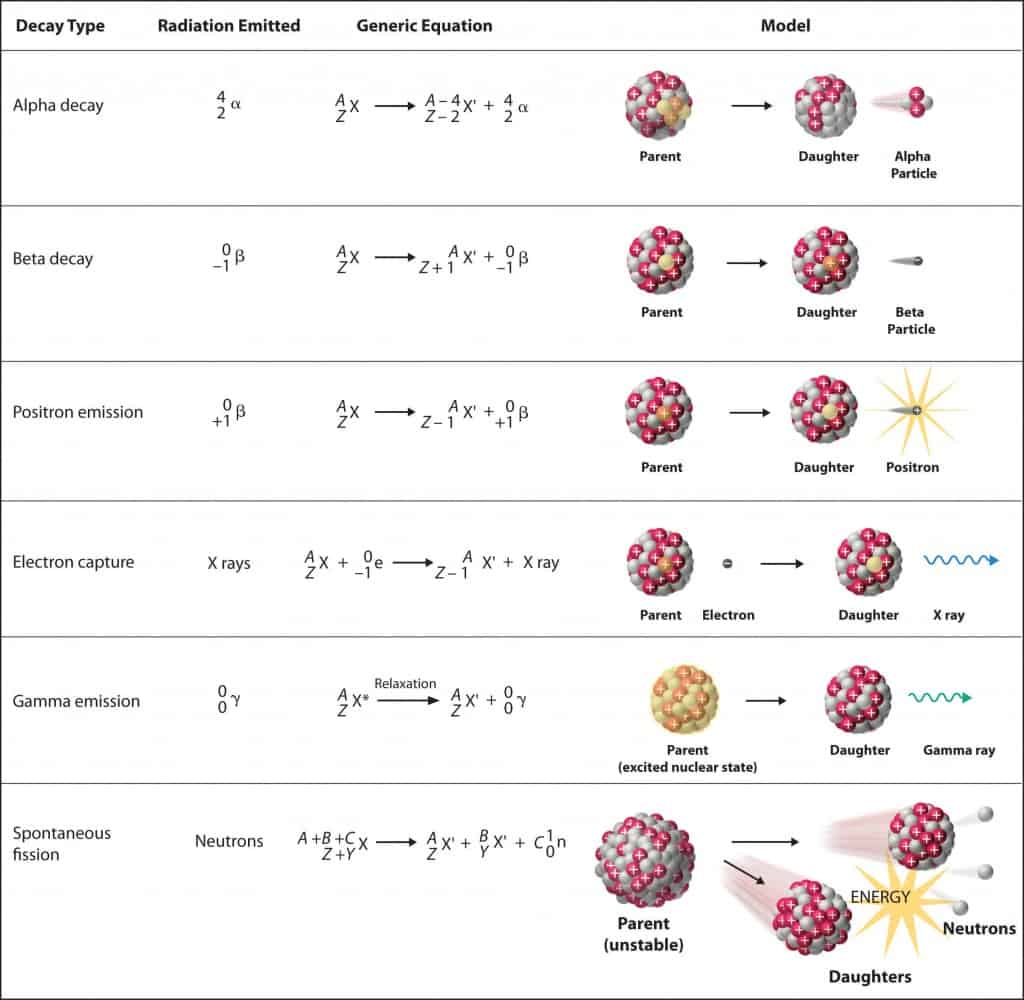
Source: chemwiki.ucdavis.edu
Instead of using the full equations in the style above, in many situations a compact notation is used to describe nuclear reactions. This style of the form a(b,c)d is equivalent to a + b producing c + d. Light particles are often abbreviated in this shorthand, typically p means proton, n means neutron, d means deuteron, α means an alpha particle or helium-4, β means beta particle or electron, γ means gamma photon, etc. The reaction above would be written as 10B(n,α)7Li.